I once visited a chemical plant where corroded metal valves were causing constant leaks and shutdowns. The manager was desperate for a solution. This is when I truly saw the power of HDPE.
High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) is ideal for industrial valves because it provides exceptional corrosion resistance, requires almost no maintenance, lasts for decades, and remains flexible under stress. These features solve the most common and costly problems found in harsh industrial environments, leading to safer and more reliable operations.
Let’s look at the specific reasons why HDPE valves are becoming the preferred choice in demanding industries.
How Does HDPE’s Corrosion Resistance Benefit Industrial Valve Applications?
Corrosion is the number one enemy of metal valves. I’ve seen stainless steel valves fail in less than a year when exposed to certain chemicals.
HDPE’s corrosion resistance benefits industrial valves by making them completely immune to rust and highly resistant to a vast range of aggressive chemicals, acids, and bases. This eliminates a major failure point, ensures consistent valve performance, and prevents product contamination in sensitive processes like chemical handling or water treatment.
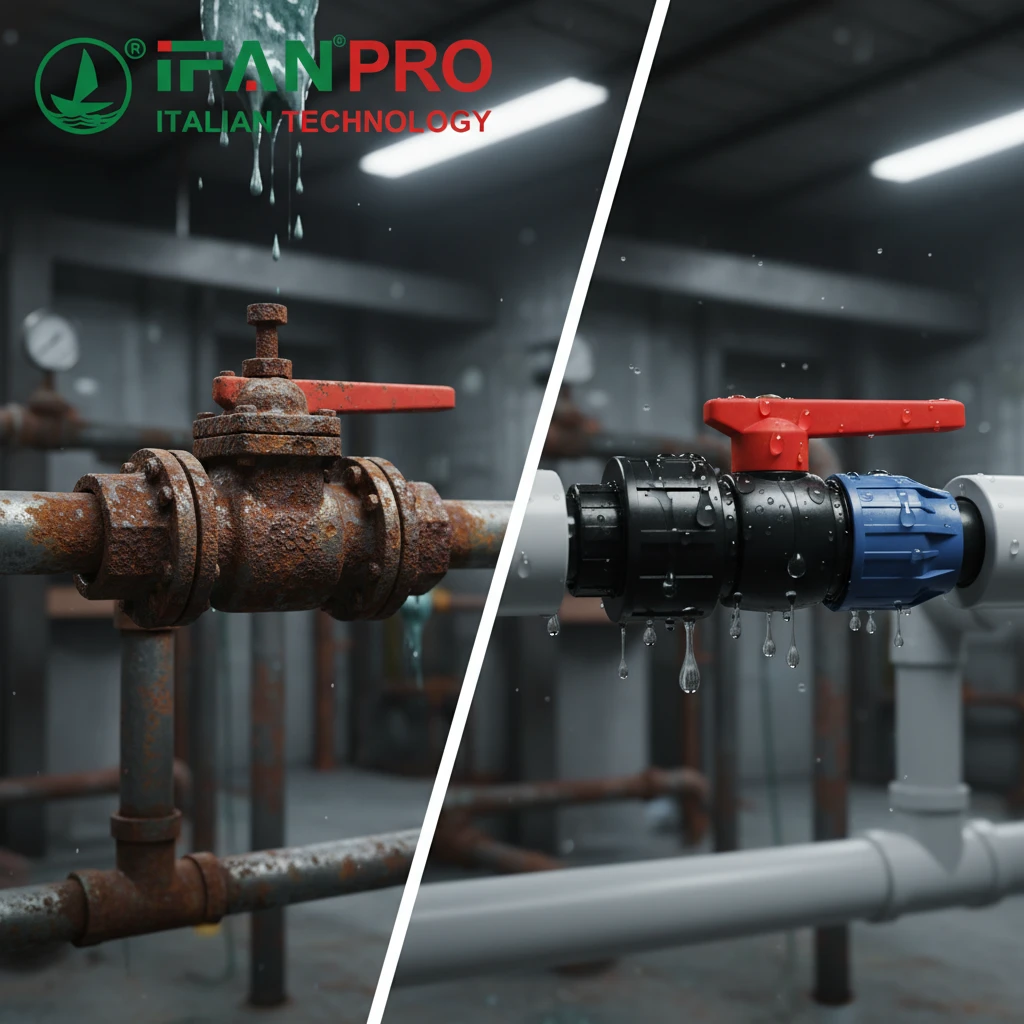

The Problem with Metals in Corrosive Environments
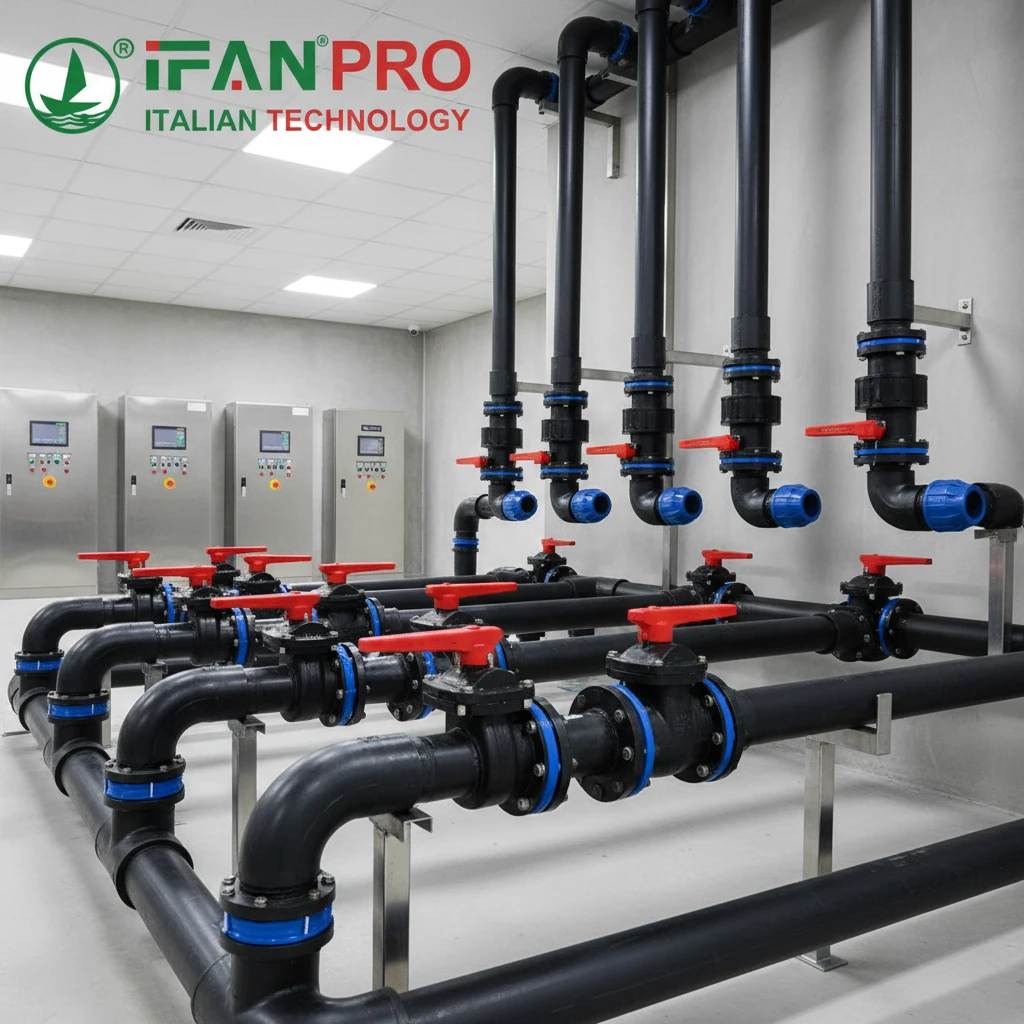
In industrial settings, valves control the flow of all kinds of substances. Many of these substances—like acids, alkalis, salts, and solvents—attack metal. Corrosion weakens valve bodies and internals. It can cause leaks, seizures, and complete failures. A leaking valve in a chemical line is not just a maintenance issue; it is a serious safety hazard. It can lead to toxic spills, environmental damage, and worker injury.
HDPE solves this problem at a fundamental level. It is a non-polar polymer with excellent chemical stability. This means it does not react with most corrosive agents. Unlike metals, it does not undergo electrochemical corrosion (rusting). The valve body, ball, or diaphragm made from HDPE will not corrode, pit, or degrade when exposed to harsh fluids.
Key Industrial Applications
This makes HDPE valves perfect for several tough applications:
- Water and Wastewater Treatment: They handle chlorinated water, ferric chloride, alum, and other treatment chemicals without corroding.
- Chemical Processing: They are safe for transporting acids, bases, and various process chemicals.
- Mining and Slurry Lines: They resist the abrasive and corrosive nature of slurry mixtures far better than lined metals.
- Marine and Offshore: They are unaffected by saltwater corrosion.
Chemical Resistance Comparison Chart
The table below shows how HDPE compares to common valve materials when exposed to common industrial chemicals.
| Chemical (at 20°C) | HDPE Valve | Stainless Steel 316 Valve | Carbon Steel Valve |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrochloric Acid (20%) | Excellent Resistance | Poor (Severe Corrosion) | Very Poor |
| Sodium Hydroxide (50%) | Excellent Resistance | Good Resistance | Fair to Poor |
| Chlorinated Water | Excellent Resistance | Fair (May Pit Over Time) | Very Poor |
| Sulfuric Acid (75%) | Good to Excellent Resistance | Poor | Very Poor |
| Salt Water (Brine) | Excellent Resistance | Good (May Pit) | Poor |
A Practical Note on Safety and Purity
Because HDPE does not corrode, it cannot introduce metal ions or corrosion by-products into the fluid stream. This is critical for industries like food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, and ultrapure water systems where fluid purity is mandatory. Choosing an HDPE valve from a certified manufacturer like IFAN ensures your process fluid stays clean and your system remains safe from corrosion-related failures.
What Makes HDPE Valves a Low-Maintenance Solution for Industrial Plants?
Unplanned maintenance stops production. I remember a plant manager telling me his team spent more hours fixing old valves than running the process line.
HDPE valves are a low-maintenance solution because their fused connections are leak-free, their smooth surfaces prevent scaling and buildup, and their corrosion-resistant material eliminates the need for repainting, coating repairs, or part replacement due to rust. This allows maintenance teams to focus on proactive tasks instead of constant emergency repairs.
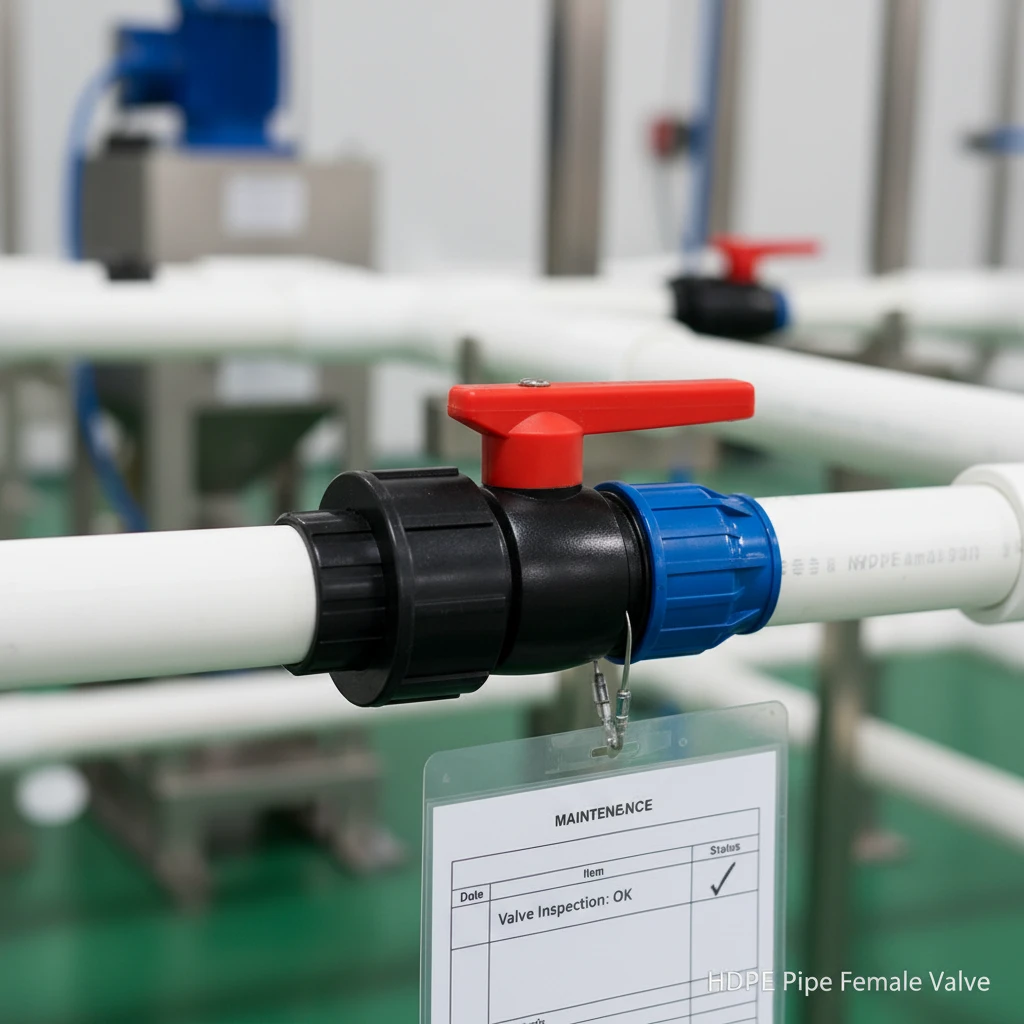

Eliminating the Biggest Maintenance Headaches
Maintenance in an industrial plant is costly. It involves labor, parts, and production downtime. Traditional metal valves create several predictable maintenance problems:
- Leaking Joints and Seals: Threaded or flanged connections on metal pipes can loosen with vibration and thermal cycles. Gaskets and seals degrade over time. HDPE systems use butt-fusion or electrofusion to create a permanent, monolithic connection that is leak-proof. There are no gaskets to replace and no bolts to re-torque.
- Internal Scaling and Clogging: In applications like wastewater or slurry, minerals and solids can build up inside metal valves, making them hard to operate or blocking them completely. The ultra-smooth bore of an HDPE valve resists scaling and adhesion, keeping the valve easy to actuate.
- Corrosion Damage: As discussed, corrosion damages metal valve bodies and internal components. This often requires partial or complete valve replacement. HDPE valves simply do not have this failure mode.
Reduced Operational Friction
The inherent properties of HDPE contribute directly to less maintenance:
- Lightweight: HDPE valves are much lighter than metal equivalents. This makes handling, installation, and any future adjustments easier and safer, reducing labor time and injury risk.
- Abrasion Resistance: For applications with suspended solids, HDPE’s abrasion resistance is superior to many metals. It doesn’t erode quickly, so the valve’s performance and sealing capability last longer.
Maintenance Task Comparison Over 5 Years
Consider the typical maintenance activities for a bank of 20 valves in a chemical transfer line:
| Maintenance Task | Carbon Steel Valves | HDPE Valves |
|---|---|---|
| Leak Repair (Gaskets/Seals) | 5-10 incidents per year | 0-1 incident (if any) |
| Actuator Binding/Jamming | Common due to corrosion buildup | Very Rare |
| External Corrosion Treatment | Annual inspection & touch-up painting | Not Required |
| Partial/Full Valve Replacement | Likely within 3-5 years due to corrosion | Unlikely in system lifespan |
| Total Estimated Maintenance Hours | 50-100 hours | <10 hours |
By drastically reducing the frequency and complexity of maintenance, HDPE valves lower operational costs and free up skilled personnel for more valuable work. The plant experiences less unexpected downtime, leading to higher overall productivity.
How Does the Longevity of HDPE Reduce Total Cost in Industrial Settings?
The cheapest valve is often the most expensive in the long run. A client saved over 60% in ten-year costs by switching to HDPE.
The longevity of HDPE reduces total cost because it eliminates frequent replacement cycles. While the initial price may be comparable, a corrosion-free, leak-free HDPE valve system can last 50+ years with minimal upkeep, avoiding the high costs of repeated purchases, installation labor, and production downtime associated with metal valve failures.
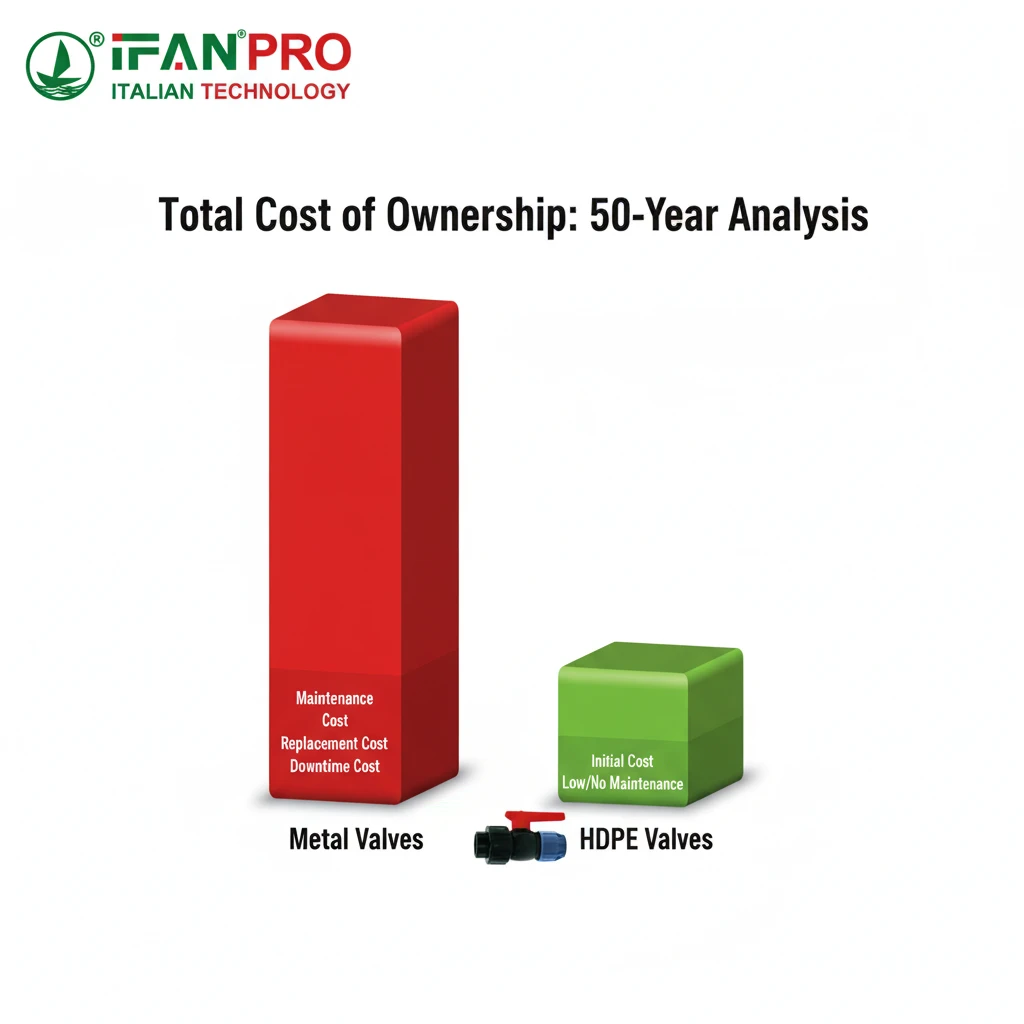
Understanding Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
Smart industrial buyers evaluate the Total Cost of Ownership, not just the purchase price. TCO includes:
- Initial Cost: Price of the valve and installation.
- Operating Cost: Energy for operation (minimal for valves), cost of any required fluid treatments.
- Maintenance Cost: Labor and parts for repairs.
- Failure/Downtime Cost: The cost of lost production during unscheduled shutdowns.
- Replacement Cost: Cost to purchase and install a new valve at the end of its life.
HDPE excels by minimizing or eliminating costs in the last three categories over an exceptionally long service life.
The Long Lifespan Advantage
HDPE is resistant to environmental stress cracking and retains its properties for decades. Manufacturers often cite a 50-year minimum service life for HDPE pressure pipes when properly installed. Valves made from the same high-quality material share this longevity. This is a stark contrast to metal valves in corrosive service, which may need replacement every 5-15 years.
Every valve replacement is a major cost event:
- Production must be stopped. Downtime costs can be thousands of dollars per hour.
- Old valve must be cut out. This involves hot work, permits, and safety procedures.
- New valve must be installed and tested. This requires skilled tradespeople and time.
With HDPE, the initial installation is often the last major intervention for that section of the system.
TCO Analysis: HDPE vs. Stainless Steel
Let’s analyze a scenario involving 10 valves in an acidic effluent line over a 30-year period.
| Cost Category | Stainless Steel Valves (316) | HDPE Valves |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Purchase & Install | $15,000 | $12,000 |
| Estimated Maintenance (30 yrs) | $8,000 (seals, actuators, repairs) | $2,000 |
| Planned Replacements | $30,000 (Replace all 10 valves twice @ $15k each) | $0 |
| Unplanned Downtime Cost | $10,000 (Estimated from leaks/failures) | $1,000 |
| Total 30-Year Cost | $63,000 | $15,000 |
| Cost per Year | $2,100 | $500 |
This table clearly shows that the longer lifespan and durability of HDPE lead to massive savings. The initial investment pays for itself many times over. The budget saved on valve replacement and downtime can be invested back into core production or other plant improvements.
Why is HDPE’s Flexibility Advantageous for Valve Networks in Dynamic Environments?
Ground shifts and thermal movement crack rigid pipes. I’ve seen HDPE valve networks absorb shifts that would have broken metal lines.
HDPE’s flexibility is advantageous because it allows the valve and piping network to absorb ground movement, thermal expansion/contraction, and water hammer pressure surges without failing. This eliminates the need for expensive expansion joints and reduces stress on valve bodies and connections, making the entire system more resilient in unstable or temperature-variable environments.
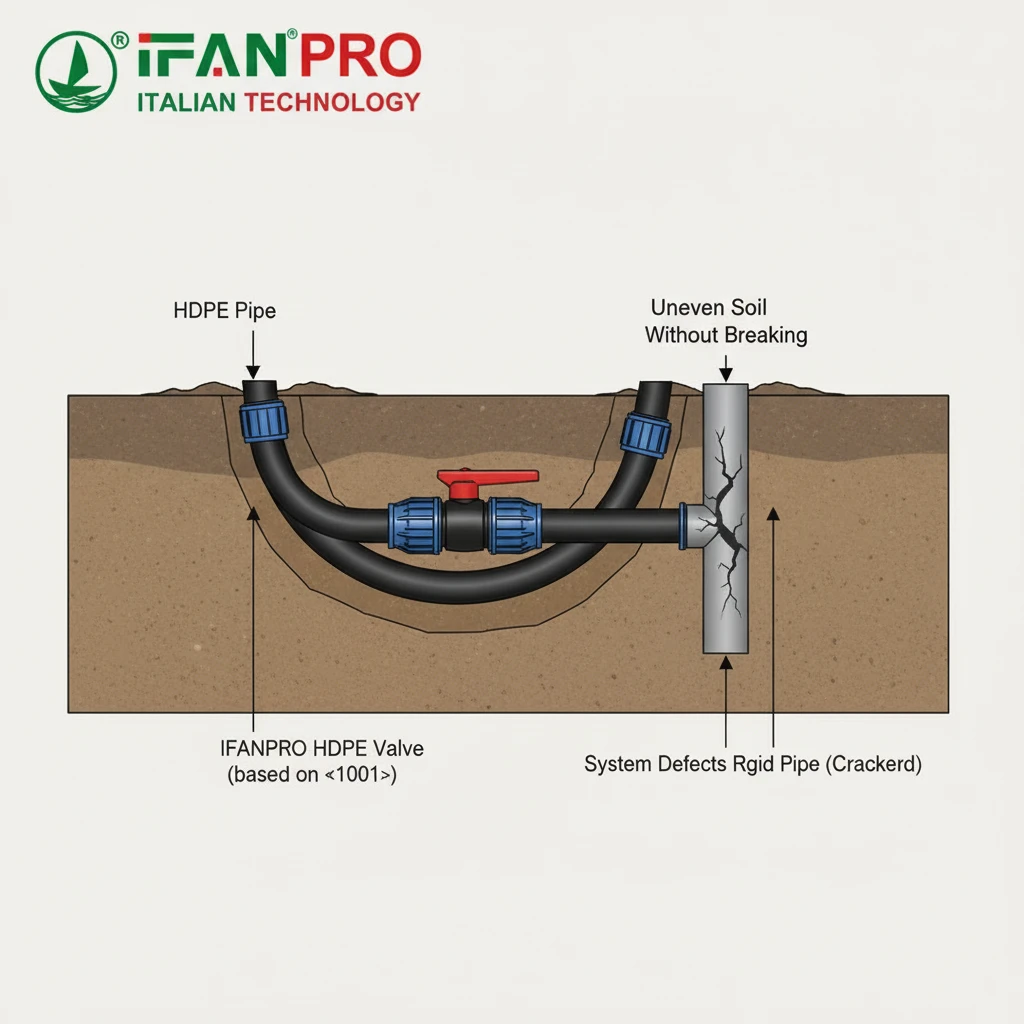
The Challenge of Dynamic Stresses
Industrial environments are not static. They create forces that stress piping systems:
- Ground Movement: Settling soil, seismic activity, or heavy traffic near buried lines.
- Thermal Expansion: Pipes and valves expand when hot and contract when cold. If rigidly constrained, this creates enormous stress.
- Water Hammer: Sudden starts and stops of pumps or fast valve closures create pressure shock waves through the fluid.
Rigid materials like cast iron or PVC cope poorly with these forces. They transfer stress directly to fittings and valves, leading to cracks, broken joints, and leaks. Engineers must add complex and costly support structures, expansion loops, or joints to manage this movement.
HDPE as a Stress-Absorbing Solution
HDPE has a high degree of flexibility and a low modulus of elasticity. This is a technical way of saying it can bend and stretch significantly without breaking. For a valve network, this means:
- Handles Ground Settlement: A buried HDPE line with integrated valves can bend and deflect as the soil settles around it. The fused joints remain intact, and the system continues to function. A rigid system would likely crack at a joint or fitting.
- Accepts Thermal Expansion: HDPE has a high coefficient of thermal expansion, but its flexibility allows it to absorb this change internally through slight snaking or bending if given minimal slack. This reduces the need for specific expansion compensation devices.
- Dampens Pressure Surges: The slight elasticity of the HDPE material acts as a cushion against water hammer. It absorbs some of the shock energy, lowering the peak pressure spike and protecting valves and pumps from damage.
Installation and Design Benefits
This flexibility translates into practical installation benefits:
- Easier Alignment: During installation, HDPE pipes and valves are easier to maneuver and align, especially in tight or congested plant areas. This speeds up installation time.
- Fewer Fittings Needed: Because the pipe can be bent to a degree, you may need fewer elbows and directional fittings. This reduces potential leak points and lowers material costs.
- Resistance to Freeze Damage: If water freezes inside an HDPE line, the pipe can expand to accommodate the ice formation and then contract back when it thaws, often without rupturing. A metal pipe would burst.
Comparison of System Behavior Under Stress
| Dynamic Stress | Rigid (PVC/Metal) System Response | Flexible HDPE System Response |
|---|---|---|
| Ground Settlement | Stress concentrates at joints, leading to cracks/breaks. | System bends/flexes, stress is distributed, joints stay sealed. |
| Thermal Cycle (Hot to Cold) | Requires expansion loops/joints to prevent buckling or pulling apart. | Absorbs movement through material flexibility; simpler anchoring. |
| Water Hammer Shock | Shock wave transmits directly, risking damage to valves and pumps. | Material absorbs/dampens some shock energy, lowering peak pressure. |
For plants built on unstable ground, in seismic zones, or with large temperature swings, specifying HDPE for valves and piping isn’t just a material choice—it’s a strategic decision for long-term system integrity and lower lifetime risk.
Заключение
HDPE valves offer unmatched corrosion resistance, low maintenance, long-term savings, and flexible durability for industrial systems. For reliable HDPE valve solutions backed by expert support, contact ИФАН. We provide high-quality HDPE ball valves, diaphragm valves, and custom fittings to meet your specific industrial needs.














Последние комментарии