I once saw a cooling system fail because a cheap clip snapped, causing pipe sag and a major leak. Choosing the right clip isn’t a small detail; it’s critical for system safety.
You select the right PVC pipe clip by accurately measuring the pipe’s outer diameter, understanding the clip’s application (like if it carries water or just holds cables), checking the strength of your mounting surface, and matching the clip’s material and load rating to your project’s specific needs and environment.
Let’s break down this process step-by-step to make sure your pipes are supported correctly and last for years.
How Do You Measure PVC Pipe Diameter for Correct Clip Sizing?
Using the wrong size clip is a common mistake. I’ve received many support calls where clips were either too tight, damaging the pipe, or too loose, letting it rattle.
You measure the PVC pipe’s outer diameter (OD) with a caliper or a flexible tape measure to get the exact size in millimeters or inches. The clip’s inner diameter (ID) should match the pipe’s OD perfectly for a snug, supportive fit without pinching or allowing movement.
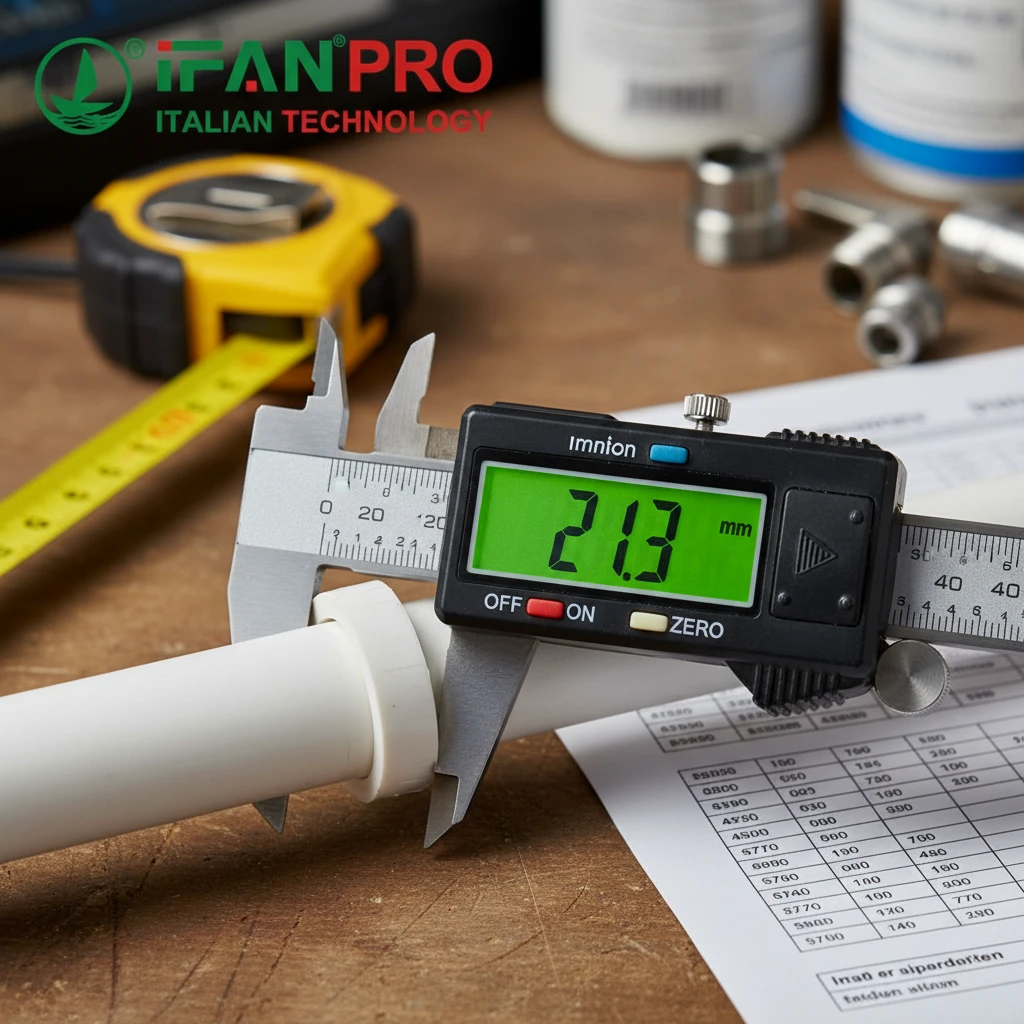

The Right Way to Measure
Getting the right size starts with a correct measurement. Never guess or use the nominal pipe size (like “1-inch pipe”), as this can be misleading. You must measure the actual physical outer diameter of the pipe.
First, find the right tool. A digital caliper is the best tool for this job. It gives you a very precise measurement. If you don’t have a caliper, you can use a flexible measuring tape. Wrap the tape around the pipe to find the circumference. Then, divide that number by 3.14 (pi) to calculate the outer diameter.
For example, if the circumference is 100mm, the outer diameter is approximately 100 / 3.14 = 31.8mm.
Understanding Clip Sizing
Once you have the pipe’s OD, you need to find a clip with a matching inner diameter (ID). A good clip should fit the pipe snugly. There should be no gap, but you also should not have to force the pipe into the clip.
A clip that is too small will strain and may not close properly. It can also compress the pipe over time, which is bad for water flow. A clip that is too large will allow the pipe to move, vibrate, and even slide out. This movement causes wear and can lead to leaks at the joints.
Standard Size Reference Table
PVC pipes and clips often come in standard metric or imperial sizes. This table can help you cross-reference common sizes.
| Nominal Pipe Size | Approximate Outer Diameter (OD) | Recommended Clip Inner Diameter (ID) |
|---|---|---|
| 1/2 inch | 21.3 mm | 21-22 mm |
| 3/4 inch | 26.7 mm | 26-27 mm |
| 1 inch | 33.4 mm | 33-34 mm |
| 1 1/4 inch | 42.2 mm | 42-43 mm |
| 1 1/2 inch | 48.3 mm | 48-49 mm |
| 2 inch | 60.3 mm | 60-61 mm |
Always remember: Measure your actual pipe. Use this table only as a guide, because manufacturing tolerances can vary.
What Role Does Pipe Application Play in PVC Clip Selection?
A clip for a garden hose is very different from one holding a pressurized water line. I advise clients to always define the application first.
The pipe’s application directly decides the clip’s type, strength, and spacing. A pressurized water line needs strong, closely-spaced clips to prevent sag and vibration. A simple cable management run only needs lightweight clips for basic support. The wrong choice can lead to system failure.

Identifying Your Application Type
You must ask: What is the pipe doing? The answer falls into a few main categories, and each one has different demands on the clip.
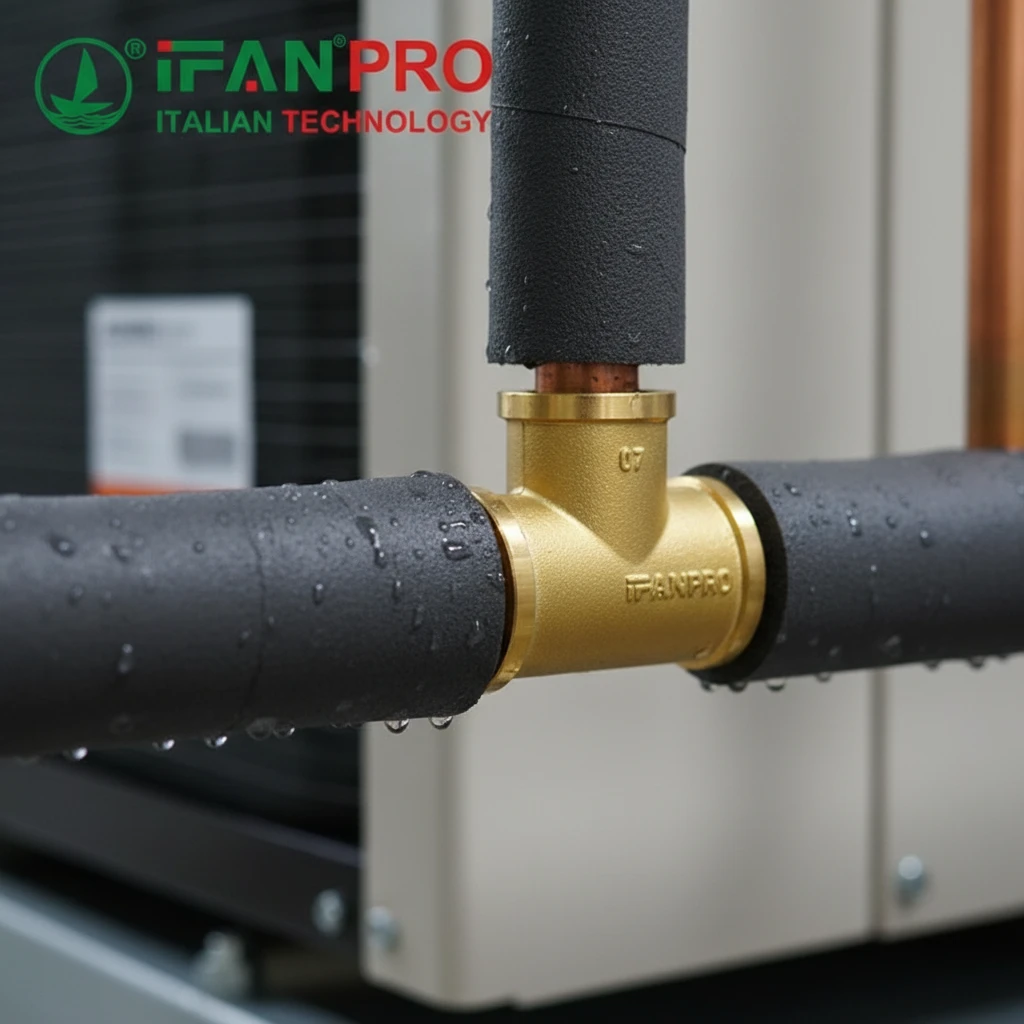
1. Pressurized Fluid Systems: This includes cold and hot water lines, irrigation systems, or compressed air lines. These pipes are under constant pressure and can experience water hammer (pressure surges). Clips for these must be very strong and rigid to prevent pipe movement, which can fatigue joints.
- Clip Choice: Use heavy-duty, fully-enclosing clips (like two-piece P-style or full-round clips) made from UV-stabilized nylon or stainless steel. Spacing between clips must be closer.
2. Drainage, Waste, and Vent (DWV): These are non-pressurized gravity-flow pipes. They are larger in diameter and often carry weight from water and waste. The main concern is preventing sagging over long runs, which can disrupt proper flow.
- Clip Choice: Use wide, sturdy saddle clips or heavy-duty brackets that support the bottom of the pipe. Material must resist corrosion from chemical vapors.
3. Conduit and Cable Management: Here, PVC pipes are used as protective sleeves for electrical wires or data cables. There is no internal pressure. The main goal is neat, secure routing.
- Clip Choice: Lightweight PVC or nylon single-screw clips, adhesive-backed clips, or cable ties with mounting holes are often sufficient. Spacing can be wider.
Application-Based Selection Guide
This table summarizes how to match the clip to the job.
| Application | Key Requirements | Recommended Clip Type | Critical Factor |
|---|---|---|---|
| Potable Water Pressure Pipe | Prevent movement/vibration, support weight of water. | Full-round nylon/PVC clip, stainless steel clamp. | Strength & Rigidity |
| Hot Water Line | Resist heat, allow for thermal expansion. | Heat-resistant nylon (PPA) or metal clips with rubber liner. | Material Temp Rating |
| Outdoor Irrigation | Resist UV rays, weathering, and corrosion. | UV-stabilized nylon, stainless steel. | Weather Resistance |
| Indoor Drain Pipe | Support heavy static load, resist chemicals. | Wide saddle clip or heavy-duty bracket. | Load Capacity |
| Electrical Conduit | Secure routing, easy installation. | PVC glue-on clip, nail-in clip, or adhesive clip. | Простота установки |
Choosing based on application prevents the most common problem: using a weak, cheap clip for a demanding job. Always think about what’s inside the pipe and what forces are acting on it.
Why is the Mounting Surface Crucial for Choosing PVC Pipe Clips?
The strongest clip is useless if it pulls off the wall. Many failures happen at the mounting point, not the clip itself.
The mounting surface is crucial because it must reliably hold the clip’s fastener and bear the pipe’s weight and dynamic forces. Choosing the wrong fastener for a surface (like using a plastic plug in drywall for a heavy pipe) is a leading cause of installation failure and safety hazards.
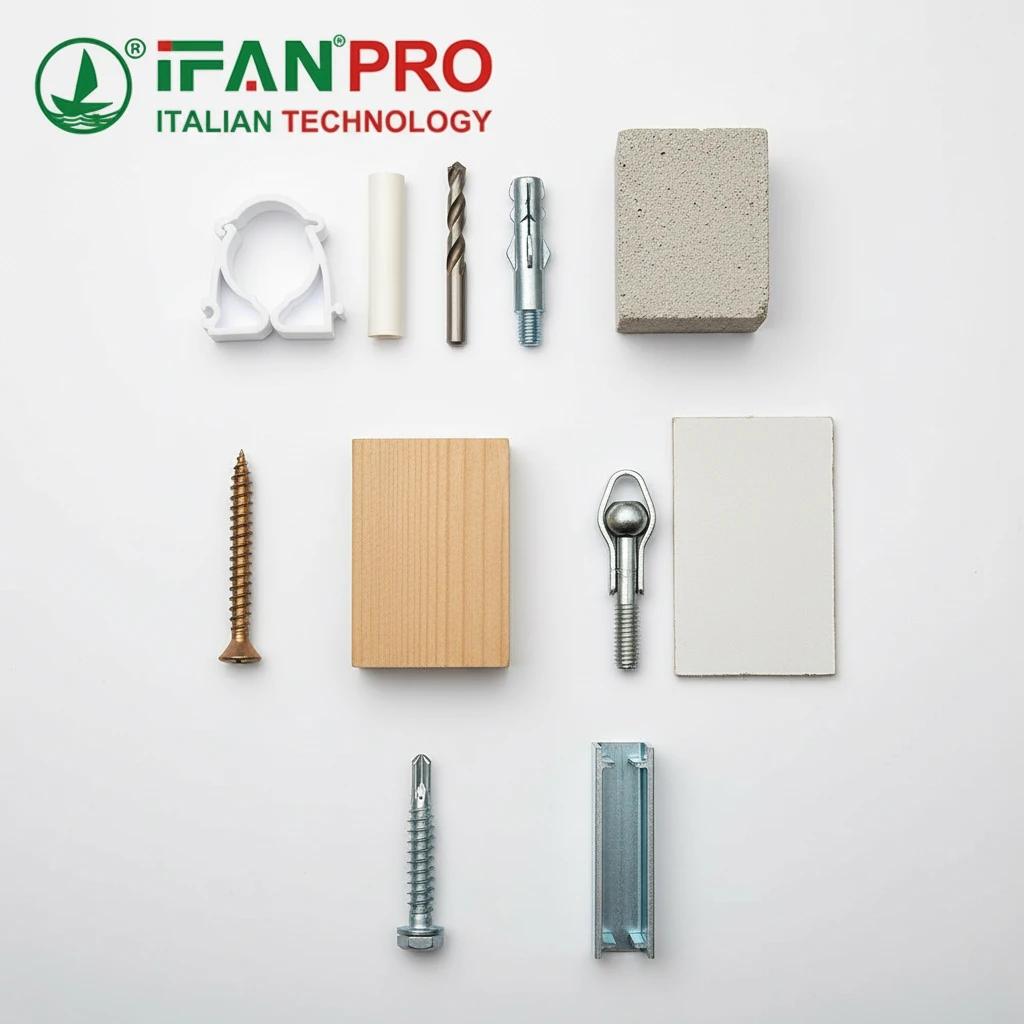

Evaluating Your Surface
Before you choose a clip, you must look at what you are screwing or gluing it to. The surface material determines everything about the mounting method.
1. Solid Surfaces: These are the best-case scenarios. They include concrete, brick, solid wood beams, and metal frames.
- How to Mount: You can use heavy-duty methods. For concrete/brick, use a hammer drill to make a hole and insert a metal wall plug (anchor), then use a screw. For wood or metal studs, you can often screw directly into them with a wood or self-tapping metal screw. These surfaces offer very high pull-out strength.
2. Hollow or Weak Surfaces: These are challenging. They include drywall (plasterboard), hollow-core doors, PVC panels, and thin plywood.
- How to Mount: You cannot rely on standard screws here. You must use special hollow-wall anchors (like toggle bolts, molly bolts, or heavy-duty plastic anchors designed for drywall). These anchors spread the load behind the surface. Always check the anchor’s weight rating. For very light loads (like a single data cable), adhesive clips might work, but be wary of temperature and cleanliness.
3. Special Surfaces: These include coated metal, tile, or outdoor siding.
- How to Mount: You may need to drill carefully. For tile, use a carbide drill bit to avoid cracking. For coated surfaces, ensure your fastener has a corrosion-resistant coating to match.
Mounting Solutions Table
Here is a guide to matching fasteners with surfaces.
| Mounting Surface | Recommended Fastener / Anchor Type | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Concrete, Brick, Stone | Metal sleeve anchor, wedge anchor, chemical anchor. | Requires hammer drill and correct drill bit size. |
| Solid Wood Beam | Standard wood screw (e.g., #8 or #10 gauge). | Screw length should be 2-3x the clip base thickness. |
| Metal Stud or Strut | Self-tapping metal screw (Tek screw), bolt & nut. | Pre-drilling a pilot hole often helps. |
| Drywall / Plasterboard | Toggle bolt, snap-toggle, heavy-duty plastic anchor. | Must use an anchor. Do not use a simple plastic plug. |
| PVC or Fiberglass Panel | Pan-head screw with a large washer. | Avoid over-tightening to prevent panel damage. |
The Rule of Spacing and Load Distribution
Even with a good fastener, you must space your clips correctly. A very heavy pipe on a weak surface may need clips spaced closer together. This spreads the total weight across more anchor points, putting less strain on each one. For long runs on drywall, it’s often better to install a horizontal wooden batten first, screwed securely into the wall studs, and then mount the clips to the wood. This transfers the load directly to the strongest part of the wall.
How Do Material and Load Ratings Affect PVC Clip Performance?
Choosing between nylon, PVC, and metal clips can be confusing. The material defines the clip’s limits in the real world.
The clip’s material and load rating directly affect its strength, temperature resistance, and longevity. A nylon clip rated for 20 lbs will fail if used on a 50 lb pipe. A standard PVC clip will deform near a heat source. Ignoring these specs leads to broken clips, sagging pipes, and costly repairs.

Understanding Clip Materials
Different materials are suited for different environments. You need to know their pros and cons.
1. PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride): This is a common, low-cost option.
- Best For: Indoor, light to medium-duty applications with no extreme temperatures. Good for cold water lines and cable management.
- Limitations: It can become brittle in freezing cold and may soften or deform if exposed to high heat (above 140°F/60°C). It has lower impact strength than nylon.
- UV Resistance: Poor. It degrades quickly in sunlight unless specifically treated.
2. Nylon (Polyamide – PA6, PA66): This is the most versatile and popular material for demanding jobs.
- Best For: Most pressurized water applications, both indoor and outdoor. It offers excellent strength, good flexibility, and impact resistance.
- Limitations: Standard nylon can absorb moisture, which slightly changes its dimensions. For hot water lines, you need a heat-stabilized grade (like PA6-G or PPA).
- UV Resistance: Good, especially in UV-stabilized black nylon formulations, which are the standard for outdoor use.
3. Metal (Stainless Steel, Galvanized Steel): This is the heavy-duty choice.
- Best For: High-temperature environments, industrial settings, corrosive areas (with stainless steel), or supporting very heavy pipes.
- Limitations: More expensive. Can be harder to install. May require a rubber or plastic liner to prevent galvanic corrosion or to cushion the pipe. Not ideal for electrical insulation.
Decoding Load Ratings
The load rating tells you how much weight the clip can safely hold. This is usually given in pounds or kilograms. It is a static load rating, meaning the weight of the pipe and its contents when not moving.
- Safety Factor: You should never use a clip at its maximum rated load. A good rule is to choose a clip with a load rating at least 1.5 to 2 times the actual weight it will support. This accounts for dynamic forces like vibration, water hammer, or accidental impact.
- How to Calculate Load: Estimate the weight of the pipe per foot, plus the weight of the water inside it. Multiply by the spacing between clips (in feet). That is the load each clip must hold.
- Example: A 1-inch PVC pipe with water weighs ~0.5 lbs/ft. If clips are spaced 4 feet apart, each clip holds about 2 lbs. You should choose a clip rated for at least 3-4 lbs.
Material Performance Comparison Table
| Материал | Typical Load Strength | Max Temp Resistance | UV/Weather Resistance | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard PVC | Low – Medium | ~140°F (60°C) | Poor | Indoor, light-duty, low-cost projects. |
| UV-Stabilized Nylon (PA6) | Medium – High | ~185°F (85°C) | Excellent | Outdoor irrigation, general pressurized water. |
| Heat-Stabilized Nylon (PPA) | High | ~220°F (105°C) | Good | Hot water lines, near heat sources. |
| Stainless Steel | Very High | >500°F (260°C) | Excellent (non-rusting) | Industrial, high-temp, corrosive environments. |
| Galvanized Steel | Very High | >500°F (260°C) | Good (but can rust) | Heavy-duty indoor/outdoor where cost is a factor. |
Always check the manufacturer’s specifications. For reliable performance in any condition, choose quality clips like those from ИФАН, which provide clear material and load rating information.
Заключение
Selecting the right PVC pipe clip requires careful attention to size, application, mounting, and material specs. For a full range of reliable, clearly-rated PVC pipe clips and clamps, trust ИФАН to support your project.













Последние комментарии