I once watched a client scramble to shut off a leaking valve in a dangerous, cramped space. That moment convinced me that remote control is not a luxury—it’s a necessity for modern operations.
A smart ball valve is the best choice for remote flow control because it allows you to open, close, or adjust fluid flow instantly from a safe, convenient location. It connects to control systems via networks, eliminates the need for manual intervention in risky areas, and provides real-time data to prevent waste and improve safety.
Now, let’s break down exactly how this technology transforms standard fluid management into an intelligent, efficient process.
How Do Wireless or Wired Networks Enable Remote Valve Operation?
Imagine turning a valve handle from your office chair. Modern networks make this possible because they act as the “nervous system” for your smart valve.
Wireless or wired networks enable remote valve operation by carrying digital command signals from a controller to an actuator on the valve. Wired networks offer stable, high-speed connections, while wireless networks provide flexible installation in existing infrastructure, which eliminates the need for extensive cabling.

Understanding the Communication Bridge
At its core, a smart ball valve is a standard valve fitted with an electric actuator and a communication module. This module acts as a translator. Specifically, it converts digital commands from your software into physical movement of the valve ball.
The network serves as the pathway for these commands. Think of it like the difference between shouting to someone across a field and calling them on a phone. The network ensures the command arrives clearly and the system acts upon it immediately.
Wired vs. Wireless: Choosing the Right Connection
Your site’s needs determine the choice between wired and wireless. Here is a simple comparison:
| Network Type | How It Works | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Wired (e.g., Modbus TCP) | Uses physical cables to connect the valve directly to the central system. | New construction or industrial plants that need ultra-reliable, fast data transfer. |
| Wireless (e.g., 4G, LoRaWAN) | Uses radio signals to send commands. The valve has a receiver/transmitter. | Remote sites or existing buildings where running cable is difficult or too expensive. |
A wired connection is often the most reliable option. It is not affected by signal interference and typically offers the fastest response time. However, installing cables over long distances can be costly and time-consuming.
The Role of Protocols and Reliability
Wireless solutions solve the cable problem. For example, technologies like LoRaWAN are great for sending simple commands over very long distances while using little battery power. Meanwhile, cellular networks offer wider coverage and can handle more data, which is useful if the valve also sends back status updates.
No matter the network type, the system uses a common language, or protocol. Protocols like Modbus or BACnet ensure that the control system’s software and the valve’s hardware understand each other perfectly. This integration allows for true automation. For instance, you can set a rule so that if a water tank level sensor reads ‘full,’ the system automatically closes the inlet valve.
Why Is Remote Control Vital for Hard-to-Reach or Hazardous Locations?
Sending a worker into a hazardous area is a risk no manager should take. Remote control turns a physical danger into a digital task.
Remote control is vital because it completely removes personnel from dangerous environments. This protects workers from exposure to toxic chemicals, extreme temperatures, or fall risks, and also allows immediate intervention in emergencies from a safe control room.
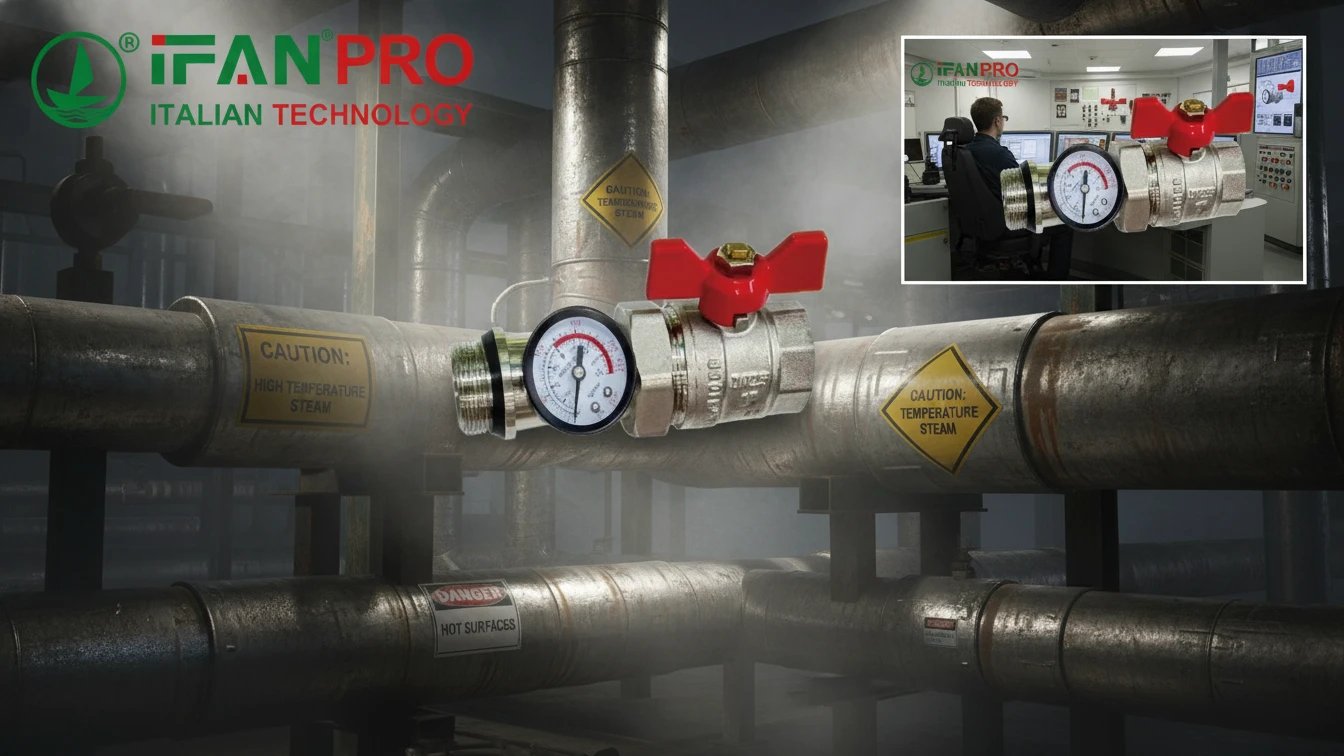

Eliminating Physical Danger
The primary benefit is safety. Many industrial valves are located in places that are dangerous for humans. Consider these common scenarios:
- Chemical Plants: Valves may be in areas with toxic gas leaks.
- High-Altitude Sites: Valves on tall towers or deep pits are risky to access.
- Extreme Temperature Zones: Areas near furnaces or in deep-freeze rooms.
Before smart valves, an operator had to suit up in protective equipment and enter these zones to manually turn a valve. This process is slow and stressful. With a remote-controlled valve, the operator can execute the same action from a safe location in seconds. This approach doesn’t just improve convenience—it actively saves lives and prevents injuries.
Solving Operational and Access Challenges
Beyond immediate safety, remote control solves major operational headaches.
First, it speeds up emergency response. If a pipe bursts in a hazardous area, every second counts. A worker might need 10-15 minutes to reach the shut-off valve. A smart valve can close with a single click in under 10 seconds, which minimizes damage.
Second, it makes routine operations efficient. Some valves need frequent operation according to a schedule. Sending someone on a long walk to turn a valve wastes time and labor. Remote control automates these routine tasks, so it frees up your team for more valuable work.
Finally, it accesses the inaccessible. Think of valves inside sealed chambers or on offshore platforms. Sometimes, reaching the valve for a simple operation is a major project. A smart valve makes these locations “virtually accessible” at any time.
Practical Example: A Wastewater Treatment Plant
Let’s look at a common application. In a wastewater treatment plant, valves control the flow of sewage and sludge.
| Task with Manual Valve | Task with Smart Remote Valve |
|---|---|
| An operator must walk to a wet, slippery, and odorous part of the plant. | The operator stays in the clean, dry control room. |
| They manually turn a large, sometimes stiff, valve handle. | They click a button on the computer screen. |
| They have potential exposure to harmful gases. | They have zero exposure to onsite hazards. |
| The process is slow and depends on staff availability. | The process is instant and you can schedule it or trigger it with sensors. |
The value is clear: remote control creates a safer, more sensible, and more efficient working environment.
How Does It Integrate with Central SCADA or Building Management Systems?
A standalone smart valve is useful, but its true power emerges when it becomes a seamless part of your larger control system.
A smart ball valve integrates with central SCADA or Building Management Systems by using standard communication protocols like Modbus TCP or BACnet. This allows the valve to appear as a data point on the central dashboard, letting operators control it directly, see its status, and incorporate it into automated sequences with other equipment.

The Power of a Common Language
Integration means the valve and the central computer system can talk to each other. They do this through software protocols, which are a set of rules for data exchange. When you choose a smart valve, you must ensure its communication protocol matches what your SCADA or BMS system understands.
Most industrial smart valves support Modbus TCP, which is very common in SCADA systems. For building automation, BACnet is the standard. This compatibility is crucial because it means you don’t need special software; the valve plugs right into the system you already use.
From Manual Control to Automated Intelligence
Once integrated, the valve transforms from a manual device into an intelligent component. Here is what becomes possible:
First, you get centralized monitoring and control. All your valves appear on a single graphic interface. You can see their real-time status and control them with a mouse click. You don’t need to remember each valve’s physical location.
Second, the system enables data logging and alarms. The system can log every valve operation. More importantly, if a valve fails to operate, it can send an immediate alarm to the control room. This allows maintenance to start before a small issue becomes a big problem.
Third, and most importantly, it allows automated process control. The valve can act based on data from other devices. For example:
- In an irrigation system, a soil moisture sensor can trigger the valve to open.
- In a factory, a high-pressure alarm can automatically close a valve to protect equipment.
- In a building’s heating system, the BMS can modulate valves based on room temperature sensors.
Integration Benefits Table
| Integration Feature | Benefit to the Operator |
|---|---|
| Single Dashboard View | Monitor and control all valves from one screen, which improves situational awareness. |
| Historical Data Tracking | Review valve operation logs for maintenance planning or process optimization. |
| Automated Sequencing | Create complex, repeatable workflows that run without human error. |
| System-Wide Alarming | Get instant alerts for valve failures or unauthorized access attempts. |
Without integration, a smart valve is just a remotely operated switch. With integration into SCADA or BMS, it becomes a data-rich, automated team player that helps you run your entire operation more smoothly.
What Are the Safety and Efficiency Benefits of Remote Flow Control?
The ultimate goal of any upgrade is to make operations safer and more efficient. Smart ball valves deliver on both fronts in measurable ways.
The safety benefits include preventing personnel exposure to hazards and enabling faster emergency response. The efficiency benefits come from automated control that eliminates manual labor, optimizes resource use, and enables predictive maintenance based on valve performance data.
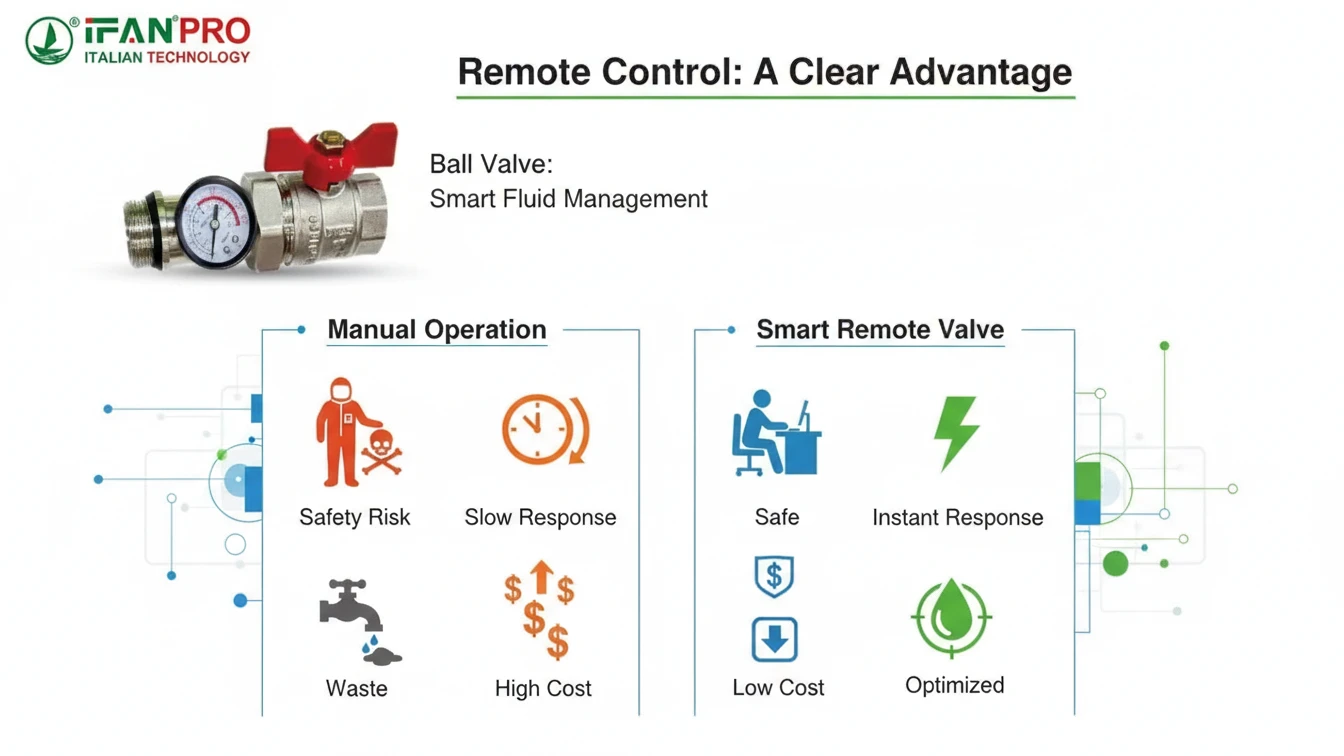
Tangible Safety Improvements
Safety is the most critical advantage, and it has direct impacts.
1. It eliminates routine hazard exposure. As discussed, keeping workers out of dangerous areas is the top benefit. This reduces accident risks, lowers insurance costs, and improves employee morale.
2. It allows rapid emergency shutdown. In case of a pipe rupture or chemical leak, you can shut off the closest valve immediately from the control room. This speed contains the incident and minimizes environmental impact. The time you save can be the difference between a minor incident and a major disaster.
3. It enables safe maintenance procedures. Maintenance teams can schedule work and remotely lock out valves in a safe position before a technician approaches. This process ensures a safe working environment.
Measurable Efficiency Gains
Efficiency gains translate directly into cost savings and better performance.
1. It saves labor and time. Manually operating dozens of valves across a facility is incredibly time-consuming. Remote control centralizes this task. Furthermore, automation handles repetitive schedules, which frees skilled staff for higher-value work.
2. It optimizes resources and reduces cost. Precise control means no waste.
- In Agriculture: Water is applied only when and where needed.
- In Manufacturing: Chemicals or gases are dosed accurately, reducing raw material costs.
- In Building HVAC: Heating flows go only to occupied zones, cutting energy bills.
3. It enables predictive maintenance and reduces downtime. A smart valve can report its number of cycles and any errors. This data allows you to schedule maintenance before a failure occurs. You replace a valve during a planned shutdown, rather than having it fail unexpectedly and cause costly, unplanned downtime.
Comparison: Traditional vs. Smart Valve Benefits
| Aspect | Traditional Manual Valve | Smart Remote-Controlled Valve |
|---|---|---|
| Safety | Operator must be on-site, exposed to potential hazards. | Operator controls from a safe, remote location. |
| Emergency Response | Slow, requires travel time to the valve location. | Instant, executed from the control room. |
| Operational Cost | High labor cost for routine operation. | Low labor cost; operations are centralized and automated. |
| Resource Use | Often leads to overuse or waste due to imprecise control. | Highly precise, automated control optimizes resource use. |
| Maintenance | Reactive (fix it after it breaks). | Predictive (monitor data and service before it breaks). |
| Data Availability | None. You don’t know the valve’s status until you check it. | Real-time status, history, and performance data available. |
In summary, the benefits go far beyond simple convenience. They create a fundamentally safer, more responsive, and more economical operation. The initial investment in smart valve technology pays for itself through avoided incidents, reduced waste, and lower labor costs.
Заключение
Smart ball valves offer unmatched safety, efficiency, and control for modern fluid management systems. For reliable, fully integratable smart ball valves, trust ИФАН to provide the right solution and full supply chain support for your project.














Последние комментарии