I once saw a technician’s plastic toolbox crack open on a job site, scattering tools and costing hours of downtime. That moment proved that the box itself is as critical as the tools inside.
The best professional toolboxes are made from materials that balance extreme durability, security, and practical function. For most heavy-duty needs, reinforced steel or heavy-duty structural plastic composites offer the best combination of impact resistance, load-bearing capacity, and long-term reliability to protect valuable tools.
The right material choice depends on your specific work environment and demands. Let’s break down the options to find the perfect match for your needs.
What Materials Offer the Best Durability for Professional Tool Boxes?
A flimsy toolbox is a liability. I’ve learned that professional durability means surviving drops, weather, and heavy loads daily.
For professional use, the most durable toolbox materials are reinforced steel (like stainless or aluminized steel), heavy-duty structural plastic polymers (such as polypropylene copolymer), and aluminum alloys. Steel offers the highest strength and security, while advanced plastics provide excellent impact resistance and corrosion immunity at a lighter weight.
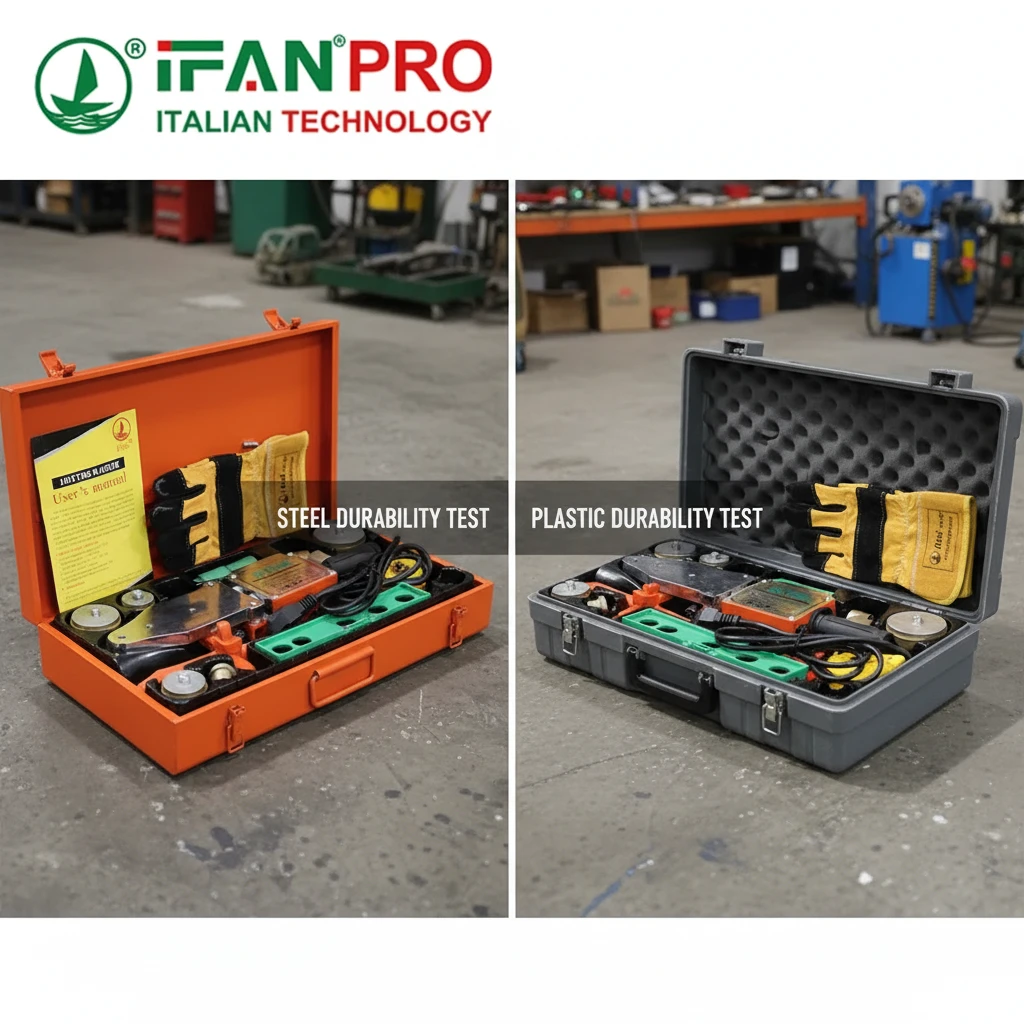

Understanding Material Strength and Application
Durability in a toolbox means it can protect your tools under tough conditions for many years. Different materials achieve this in different ways. The best choice comes from understanding their core strengths.
First, let’s talk about steel. Steel is the classic choice for a reason. It has very high tensile strength. This means it can carry heavy loads without bending. A steel toolbox won’t deform under the weight of many metal tools. It also offers superior security. Steel is very difficult to break into, which is important for expensive tool collections. However, not all steel is the same.
Key Durable Materials Compared
Here is a breakdown of the top materials:
| Материал | Best For | Key Durability Traits | Main Weakness |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reinforced Steel | Heavy-duty industrial sites, mobile workshops. | Maximum load capacity, high security, dent-resistant. | Can rust if coating is damaged; very heavy. |
| Structural Plastic (PP Copolymer) | Electrical work, outdoor/ wet environments, daily commute. | Won’t rust or corrode; excellent impact resistance; lighter weight. | Can warp under extreme, constant heat; lower load limit than steel. |
| Aluminum Alloy | Aviation, HVAC, where weight is a major concern. | Strong yet lightweight; naturally corrosion-resistant. | More expensive; can dent more easily than steel. |
| Sheet Metal | Light-duty, budget-conscious general use. | Low cost, readily available. | Dents and rusts easily; not for professional heavy use. |
Second, modern plastics have changed the game. Today’s high-quality toolboxes use materials like polypropylene copolymer. This material is engineered for toughness. It can flex on impact instead of cracking. This makes it perfect for environments where the box might get knocked over. Also, plastic will never rust. This is a huge advantage for plumbers, electricians, or anyone working near water or chemicals.
Third, we have aluminum. Aluminum toolboxes are very strong for their weight. They are much lighter than steel, which is important if you carry your toolbox up ladders or load it in a truck every day. They also resist corrosion naturally. The trade-off is that aluminum is softer than steel, so it can dent more easily and is often more expensive.
In summary, for the ultimate in strength and security, choose steel. For a lighter, rust-proof, and impact-resistant option, choose a high-quality structural plastic. For the best strength-to-weight ratio, consider aluminum.
How Does Steel Compare to Plastic for Heavy-Duty Tool Storage Needs?
Choosing between steel and plastic is a common dilemma. I advise clients based on their daily grind, not just a catalog spec.
Steel is superior for ultimate load-bearing capacity, security, and stability under massive weight, making it ideal for large mechanic’s tool chests. Heavy-duty plastic excels in impact resistance, corrosion immunity, and lighter weight, making it better for field service technicians, electricians, and those who need to carry their tools frequently.
The Case for Steel Toolboxes
Steel is the traditional king of heavy-duty storage for several key reasons. Its primary advantage is sheer structural strength. Steel boxes can support hundreds of pounds of tools without the drawer slides failing or the body sagging. This is why you see steel used for large rolling cabinets in auto shops.
Next, steel offers unmatched security. The material itself is difficult to cut or pry open. Combined with robust locks, a steel toolbox keeps your investment safe from theft. Furthermore, steel has a high tolerance for heat. It won’t warp or soften if left in a hot van or near a workshop heat source.
However, steel has downsides. The most obvious is weight. An empty steel box is heavy, and a full one can be extremely difficult to move. The other major risk is corrosion. If the paint or powder coating chips and the metal is exposed to moisture, it will rust. This requires maintenance and care.
The Case for Heavy-Duty Plastic Toolboxes
Modern engineering plastics have created a powerful alternative. The best plastic toolboxes are made from thick, molded polypropylene with aluminum or steel reinforcement at stress points.
The biggest advantage of plastic is impact resistance. When dropped or struck, a good plastic toolbox will often bounce or dent instead of cracking. It is also completely immune to rust and corrosion. You can use it in salty, wet, or chemical environments without worry. Additionally, plastic is a natural insulator, which can be a safety benefit for electrical tools.
The main limitations are weight capacity and heat. Plastic boxes have a lower maximum load rating than comparable steel boxes. They can also warp if exposed to sustained, direct high heat (like being left in the sun on a black asphalt driveway all summer).
Decision Guide: Steel vs. Plastic
This table helps you choose based on your primary needs:
| Your Priority | Recommended Material | Reason |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum Tool Security & Theft Deterrence | Steel | Harder to break into physically. |
| Carrying Tools to Different Job Sites Daily | Heavy-Duty Plastic | Lighter weight and impact-resistant for transit. |
| Storing Extremely Heavy Tools (e.g., large power tools) | Steel | Higher load-bearing capacity for drawers and shelves. |
| Working in Wet, Corrosive Environments | Heavy-Duty Plastic | Will not rust, ever. |
| Need for a Mobile Workbench Surface | Steel | Provides a stable, hard surface for tasks. |
| Budget-Friendly Heavy-Duty Option | Пластик | Often provides good durability at a lower cost than premium steel. |
In conclusion, if your toolbox stays in one secure location and holds very heavy items, steel is likely best. If you are constantly on the move, facing weather and bumps, a high-quality plastic toolbox will likely serve you better and be easier on your back.
Why is Impact Resistance Important When Selecting a Tool Box Material?
A toolbox falling from a truck bed shouldn’t mean a ruined workday. Impact resistance is about real-world accidents.
Impact resistance is crucial because it determines whether a toolbox survives common accidents like being dropped, knocked over, or struck by other equipment without cracking or breaking open. A box that fails on impact can lead to lost tools, job delays, and costly replacements, making impact resistance a key factor for any mobile professional.
The Real-World Cost of a Failed Box
Impact resistance is not a minor feature; it is a core requirement for functionality. Think about how a toolbox is used. It gets loaded in and out of vehicles, pushed across rough ground, and sometimes tipped over. In a busy workshop, it might get bumped by a cart.
If the material is brittle and cracks on impact, the immediate result is often spilled tools. This causes lost time as you pick everything up. Worse, small or expensive tools can be lost entirely. At that moment, the toolbox has failed its only job: to keep your tools safe and organized. Furthermore, a cracked box is often unusable, forcing you to buy a replacement immediately.
How Different Materials Handle Impact
Different materials absorb and handle shock in different ways. Understanding this helps you choose wisely.
- Steel: Steel handles impact through deformation. When hit, a steel box will typically dent. This can look bad, but the box usually remains sealed and functional. The integrity of the container is maintained. However, a very severe impact on a corner or seam could potentially crack a weld.
- Structural Plastic: Good quality plastic handles impact through flexing and absorption. The material is designed to have some give. When dropped, it absorbs the energy and may bounce. This often prevents permanent damage altogether. A very hard impact might cause a scuff or a small crack, but high-quality polymers are engineered to resist this.
- Thin Sheet Metal or Low-Quality Plastic: These are the worst for impact. Thin metal will dent severely and easily, potentially jamming drawers or lids. Cheap, brittle plastic will shatter or split open upon a serious drop, catastrophically failing.
Features that Enhance Impact Resistance
Material choice is the first step, but design also plays a big role.
| Design Feature | How It Improves Impact Resistance |
|---|---|
| Rounded Corners | Distributes impact force over a wider area instead of concentrating it on a sharp corner, which is a common failure point. |
| Reinforced Ribbing | Molded ridges or ribs in plastic boxes add structural strength, much like an I-beam, preventing flex and crack propagation. |
| Internal Frame | Some plastic boxes have a steel or aluminum frame inside the molding, offering the impact resistance of plastic with the skeletal strength of metal. |
| Thick Wall Construction | Simply using more material (thicker gauge steel or plastic walls) makes any box more resilient to dents and cracks. |
In short, prioritizing impact resistance means choosing a toolbox that is your reliable partner through the bumps and knocks of daily work. It saves you money, time, and frustration in the long run. For most professionals who transport their tools, it should be a top-three selection criteria.
What are the Key Features of a Water-Resistant Industrial Tool Box?
Water damage ruins tools. I’ve seen rusted socket sets and corroded electronics from just one incident with a leaky box.
A water-resistant industrial tool box must have a continuous lid seal, waterproof gasketing, sealed seams and drains, and a design that prevents water ingress even when pressurized (e.g., from a hose or heavy rain). True water resistance protects tools from rust, corrosion, and electrical damage, extending their lifespan significantly.
Defining True Water Resistance
For professionals working outdoors, on ships, or in damp industrial settings, water resistance is non-negotiable. It’s more than just a lid that closes tightly. A truly water-resistant box is engineered to keep water out under challenging conditions.
The most important feature is a high-quality perimeter seal. This is usually a rubber or foam gasket that runs continuously around the opening where the lid meets the body. When the lid latches shut, it compresses this gasket, creating a watertight barrier. The quality and thickness of this gasket are critical.
Essential Design Elements
Beyond the seal, several other design elements work together to keep tools dry.
First, look at the drain. This might sound strange, but the best waterproof boxes often have plugged drain holes. Why? If water gets inside (from condensation, for example), you need a way to let it out. These boxes have small holes at the bottom corners with removable rubber plugs. You can open them to drain any moisture, then seal them shut for full protection.
Second, examine the seams. On a plastic box, the body should be molded as one single piece to avoid seam leaks. On a metal box, critical seams should be continuously welded, not just spot-welded, and then sealed with a waterproof coating.
Third, consider the latches and hardware. The points where latches and handles attach should have gaskets or seals behind them. Otherwise, water can seep in through the bolt holes.
Checklist for Water-Resistant Toolboxes
Use this table to evaluate a toolbox’s water-resistant claims:
| Feature | What to Look For | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Lid Gasket | A full-perimeter, compressible rubber seal. It should be firmly glued in place. | Creates the primary seal against rain and splashes. |
| Latch Points | Latches that pull the lid down tightly to compress the gasket evenly. | Ensures consistent seal pressure all around the lid. |
| Drain System | One or more drain holes with snug-fitting rubber plugs at the lowest point. | Allows condensation or incidental water to be drained out. |
| Seam Construction | Minimal seams on the main body. On metal boxes, smooth, welded seams. | Prevents water ingress through the weakest structural points. |
| Vent Valve (Optional) | A one-way vent valve that allows air pressure to equalize without letting in water. | Prevents a vacuum seal that makes the box hard to open, especially after altitude or temperature changes. |
Finally, the material itself contributes. As mentioned, plastic does not rust. Even if a small amount of moisture gets inside a plastic box, the box itself won’t be damaged. A steel box must have a superior internal and external coating to prevent rust from starting in a humid environment.
In summary, don’t just trust a marketing term. Look for the physical features—the seal, the drains, the sealed seams—that guarantee your tools will stay dry through a storm, a washdown, or a wet worksite.
Заключение
The best toolbox material balances strength, weight, and resistance to your specific job-site hazards. For durable, well-designed storage solutions that meet these professional demands, explore the range of industrial toolboxes from ИФАН.













Последние комментарии