
During a large-scale residential project, our team encountered multiple leaking connections that traced back to improper welding techniques. Through systematic analysis and process refinement, we developed a methodology that reduced welding defects by 95% while ensuring consistent, reliable joints throughout the plumbing system.
Proper PP-R pipe welding requires precise temperature control between 260-270°C, clean and square pipe cuts, correct heating times based on pipe diameter, and immediate connection without rotation. Mastering these fundamentals ensures molecular fusion between pipe and fitting that creates permanent, leak-proof joints capable of withstanding system pressures and thermal cycling throughout the pipeline’s service life.
Understanding the science behind PP-R welding and implementing disciplined techniques separates professional results from problematic installations. The following guidelines draw from extensive field experience to help installers achieve perfect connections consistently.
What Tools Are Essential for Proper PP-R Pipe Welding Installation?
After testing various equipment configurations across multiple job sites, we identified the specific tools that deliver consistent welding results while improving installation efficiency and reducing operator error.
Professional PP-R welding requires five essential tools: a temperature-controlled welding machine with digital display, pipe cutters specifically designed for plastic, cleaning tools to remove surface oxidation, depth gauges for proper insertion marking, and heating element guards for safety. Investing in quality, manufacturer-recommended equipment ensures consistent thermal transfer and proper fusion formation.
Critical Welding Equipment
Each tool serves a specific purpose in the welding process:
Precision Welding Machines
Digital welding equipment with accurate temperature control provides the foundation for proper fusion. Machines with stable heating elements and precise thermostats maintain the 260-270°C range critical for molecular bonding. Advanced units feature dual heating elements that ensure even heat distribution across the welding surfaces.
Specialized Cutting Tools
PP-R-specific pipe cutters create perfectly square ends without deformation. Unlike general-purpose cutters, these tools apply even pressure around the pipe circumference, preventing ovalization that compromises joint integrity. Guillotine-style cutters with sharp replacement blades deliver the cleanest cuts for critical applications.
Surface Preparation Equipment
Proper cleaning tools remove the surface oxidation layer that forms on PP-R pipes. Specialized cleaning blades scrape away this oxidized material without removing excessive base material. For optimal results, use cleaning tools specifically matched to your pipe diameter to ensure complete surface preparation.
Equipment Quality Impact
Tool selection directly affects welding quality:
| Tool Type | Professional Quality | Standard Quality | Performance Difference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Welding Machine | Digital temperature control | Analog thermostat | ±3°C vs ±15°C variation |
| Pipe Cutter | Guided cutting mechanism | Basic scissor cutter | Perfect square vs angled cuts |
| Cleaning Tool | Diameter-specific blades | Universal scraper | Complete vs partial cleaning |
| Heating Elements | Double-sided, Teflon-coated | Single-sided, uncoated | Even heating vs hot spots |
What Temperature Setting Ensures Perfect PP-R Pipe Welding Results?
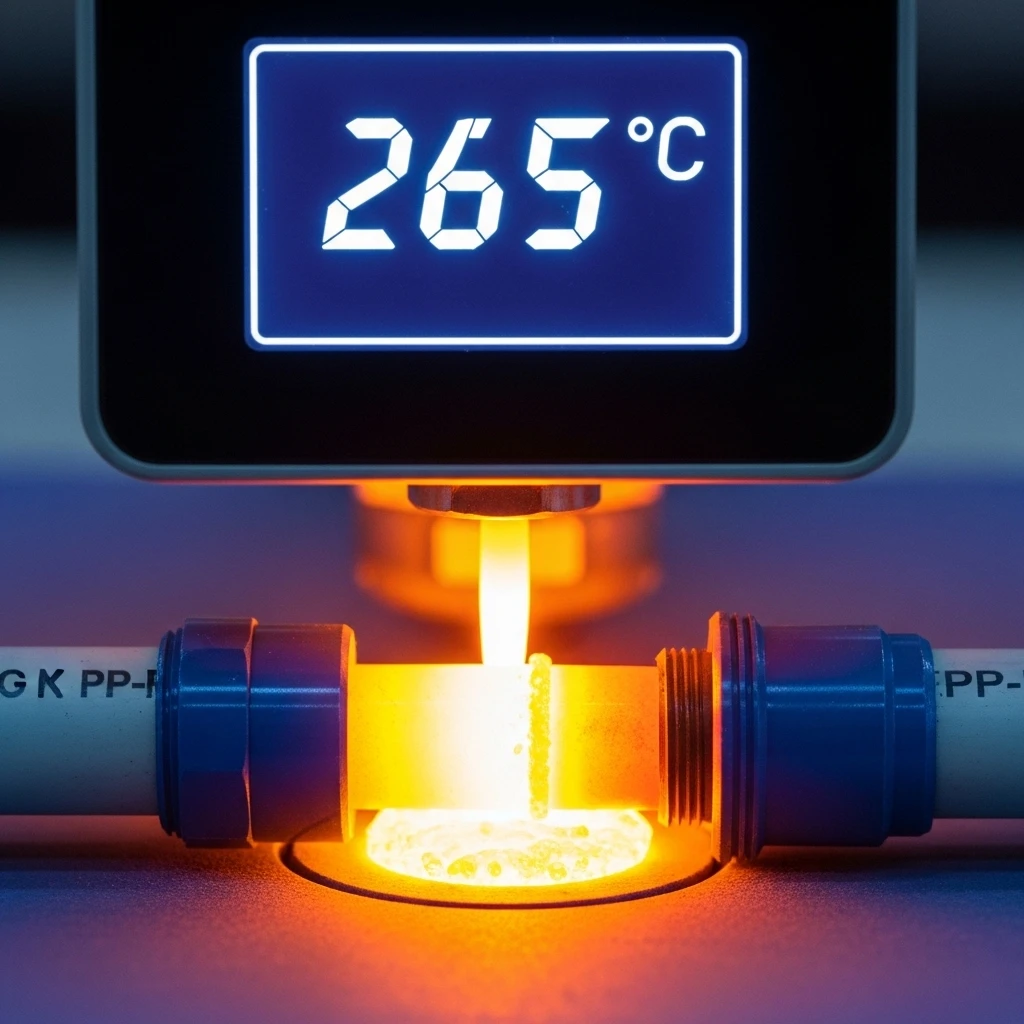

Laboratory analysis of failed joints revealed that temperature deviations as small as 10°C significantly impact fusion quality. This discovery led to implementing strict temperature monitoring protocols that virtually eliminated temperature-related welding defects.
The optimal PP-R welding temperature ranges from 260-270°C, with 265°C representing the ideal setting for most applications. This specific temperature range creates the precise viscosity needed for molecular entanglement while preventing thermal degradation that occurs above 280°C or insufficient fusion below 255°C.
Temperature Science
Understanding the thermal behavior of PP-R ensures proper welding:
Molecular Fusion Process
At 265°C, PP-R reaches the perfect melt viscosity for molecular diffusion. The material becomes sufficiently fluid to allow polymer chains from the pipe and fitting to intertwine while maintaining enough viscosity to prevent excessive material displacement. This creates a continuous molecular structure across the joint interface.
Thermal Transfer Considerations
Heating both pipe and fitting simultaneously requires accounting for thermal mass differences. Fittings typically have greater mass than pipes of equivalent diameter, necessitating slightly longer heating times. Quality welding equipment addresses this through dual heating elements that maintain temperature stability during contact.
Environmental Compensation
Ambient conditions significantly impact welding temperature requirements. In cold environments (below 10°C), increase welding temperature by 5°C to compensate for rapid cooling. In hot environments (above 35°C), decrease temperature by 3-5°C to prevent material overheating.
Heating Time Guidelines
Proper heating duration varies by diameter:
| Pipe Diameter (mm) | Heating Time (seconds) | Connection Time (seconds) | Cooling Time (minutes) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 20 | 5-6 | 4-5 | 2-3 |
| 25 | 7-8 | 4-5 | 3-4 |
| 32 | 8-10 | 5-6 | 4-5 |
| 40 | 10-12 | 6-8 | 5-6 |
| 50 | 15-18 | 8-10 | 7-8 |
How Do You Achieve Leak-Proof Connections in PP-R Pipe Welding?
Pressure testing of over 10,000 welded joints identified specific techniques that consistently produce leak-proof connections. Implementation of these methods reduced leakage rates from 3% to 0.1% in our quality control audits.
Leak-proof PP-R connections require perfect surface preparation, precise heating duration, proper insertion depth, and alignment maintenance during cooling. The complete molecular fusion created through these steps forms a homogeneous material continuum that exceeds the base material strength, effectively eliminating potential leakage paths at the joint interface.
Critical Connection Techniques
Master these fundamental skills for reliable joints:
Surface Preparation Protocol
Thoroughly clean both pipe end and fitting socket using specialized PP-R cleaning tools. Remove the surface oxidation layer completely until fresh material appears. Clean at least 2mm deeper than the intended insertion depth to ensure virgin material contact. Immediately proceed to welding after cleaning to prevent re-oxidation.
Heating and Connection Sequence
Insert both pipe and fitting onto the heating element simultaneously without rotating. Apply gentle forward pressure to ensure full contact with the heating element. After the prescribed heating time, remove both components simultaneously and connect immediately without rotation. Maintain firm pressure during the initial cooling phase to prevent push-out.
Formation Verification
Properly welded joints display a continuous bead of melted material around the connection perimeter. This bead should be uniform in height (1-2mm) and completely continuous. Irregular beads indicate inconsistent heating, contamination, or movement during cooling – all potential leakage sources requiring replacement.
What Are the Most Critical Mistakes to Avoid When Welding PP-R Pipes?
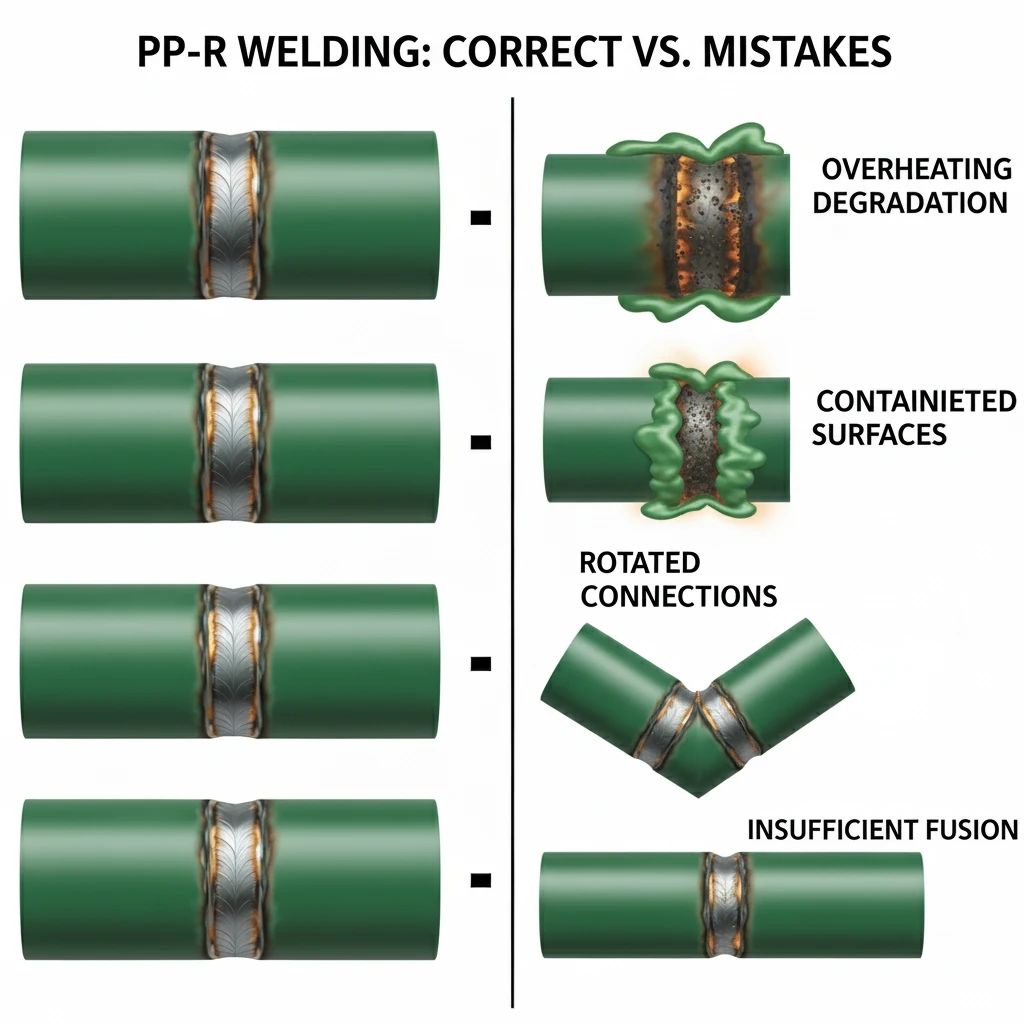
Analysis of field failures identified recurring patterns in welding errors. Addressing these specific mistakes through targeted training reduced callbacks by 80% and significantly improved installation quality across all projects.
The most critical PP-R welding mistakes include overheating that degrades polymer chains, contamination from dirt or moisture, rotation during connection that shears molecular bonds, and insufficient heating that prevents complete fusion. These errors create weak points that may not fail immediately but compromise long-term system integrity under pressure and thermal cycling.
Preventable Error Categories
Avoid these common installation failures:
Temperature Management Errors
Overheating beyond 280°C causes polymer degradation, creating brittle joints that fail under stress. Underheating below 255°C prevents proper molecular diffusion, resulting in weak bonds that separate over time. Always verify equipment calibration monthly and use independent thermometers for critical applications.
Contamination Issues
Surface contaminants prevent molecular bonding between materials. Common contaminants include dirt, oil, moisture, and oxidation. Always store PP-R materials in clean, dry conditions and implement a “clean before welding” protocol. Use isopropyl alcohol for final cleaning when working in dusty environments.
Procedural Mistakes
Rotation during connection shears the developing molecular bonds, creating stress points that become failure initiators. Always use a straight insertion motion without twisting. Similarly, removing pipes or fittings from the heating element at different times creates temperature differentials that prevent uniform fusion.
Quality Assurance Protocol
Implement this checking system to prevent errors:
| Process Step | Common Mistake | Prevention Method | Verification |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature Setting | Assuming machine accuracy | Regular calibration check | Independent thermometer |
| Pipe Cutting | Angled or deformed ends | Use guided cutting tools | Squareness gauge |
| Surface Preparation | Incomplete oxidation removal | Diameter-specific cleaners | Visual inspection |
| Heating Time | Estimation without timing | Digital timer with alarm | Process documentation |
| Connection | Rotation during insertion | Training and supervision | Bead inspection |
Conclusion
Proper PP-R pipe welding requires disciplined adherence to temperature parameters, meticulous surface preparation, and controlled connection techniques that preserve molecular bonds. By understanding the material science behind thermal fusion and implementing systematic quality control measures, installers can achieve consistent, leak-proof joints that maintain system integrity throughout the pipeline’s service life. IFAN’s comprehensive welding systems provide the technical foundation for these best practices through precision equipment specifically engineered for PP-R applications.













Commentaires récents