I once visited a client whose water treatment plant faced constant pump overruns and a major pipe burst. Their manual valves couldn’t react in time. The financial loss was staggering, and it convinced me of the power of automation.
Yes, smart valve automation significantly reduces operational costs. It achieves this by providing precise control to cut energy and water waste, enabling predictive maintenance to avoid expensive failures, slashing labor needs through remote management, and proactively preventing leaks that cause costly damage and loss. This transforms valves from simple shut-off devices into strategic assets for saving money.
Let’s break down exactly how smart valves deliver these substantial cost savings across different areas of your operation.
How Does Precise Control Minimize Energy or Pumping Costs Directly?
Many plants run pumps longer or harder than needed because their valves can’t adjust flow precisely. I’ve seen energy bills where 30% of the cost was pure waste from this overcompensation.
Precise control from smart valves minimizes energy costs by automatically adjusting flow rates and pressure to match the exact, real-time demand of the system. This prevents pumps from working harder than necessary, eliminates pressure spikes, and optimizes the entire system’s efficiency, directly reducing electricity consumption and pump wear.
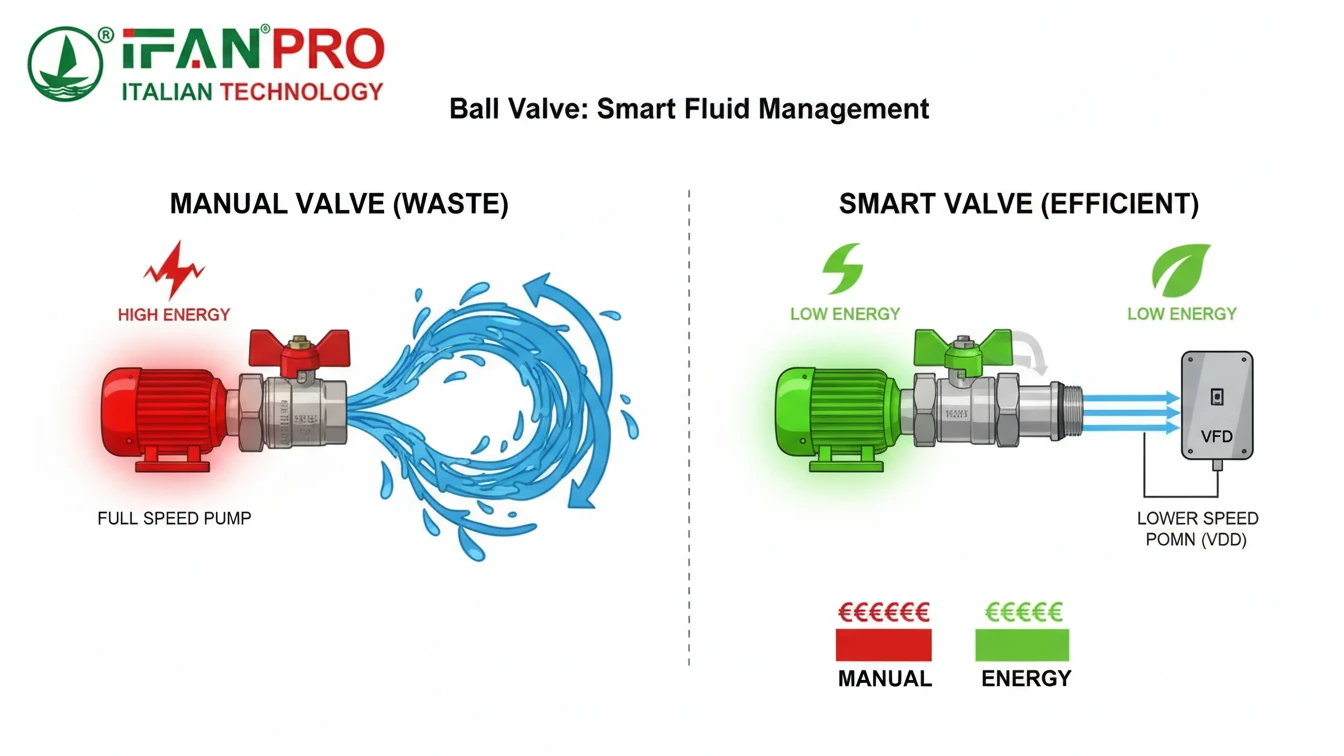
The Problem of “Always-On” Systems
In traditional setups with manual or basic valves, systems often operate in a wasteful “always-on” or “full-blast” mode. For example, a pump might run at a fixed speed to push water through a partially open manual valve. This is like driving your car with one foot on the gas and the other on the brake—you waste fuel and strain the engine.
Smart valves, connected to sensors and a control system, change this completely. They act like a precise accelerator for your fluid flow.
How Smart Valves Achieve Precision
First, they respond in real-time. If a sensor detects lower demand in a building’s heating loop, the smart valve can modulate closed slightly to reduce hot water flow immediately. The pump then needs to provide less pressure, which consumes less electricity. This is called demand-based control.
Second, they maintain optimal pressure. Smart valves can be integrated with variable frequency drives (VFDs) on pumps. The valve and pump communicate to maintain the perfect pressure, eliminating wasteful pressure spikes that strain pipes and equipment.
Direct Impact on Energy Bills
The savings come from two places:
- Reduced Pump Runtime: Pumps don’t have to run at full capacity all the time.
- Higher System Efficiency: The entire system works in harmony, removing bottlenecks and over-pressure points.
Cost Comparison: Traditional vs. Smart Valve System
| Cost Factor | Traditional Manual Valves | Automated Smart Valves |
|---|---|---|
| Pump Energy Consumption | High. Constant high-speed operation against fixed resistance. | Low. Speed adjusts to match real-time, valve-optimized demand. |
| Peak Demand Charges | Often high due to pumps starting against closed valves. | Reduced through soft starts and controlled ramp-ups. |
| Pump Maintenance | More frequent. Bearings and seals wear out faster under constant stress. | Less frequent. Smooth operation extends equipment life. |
| Water/Process Fluid Waste | Higher likelihood due to imprecise control and over-pressurization. | Minimized through exact flow control. |
In short, precise control turns your fluid system from a blunt instrument into a finely tuned orchestra. Every movement is efficient, and no energy is wasted overcoming unnecessary resistance. The result is a direct and measurable reduction in your utility bills.
How Does Predictive Maintenance Reduce Downtime and Repair Expenses?
Unexpected valve failure is a nightmare. I recall a factory that had to shut down for two days because a critical valve seized. The repair bill was high, but the lost production cost was ten times higher.
Predictive maintenance reduces downtime and repair costs by using smart valve diagnostics to monitor performance—like cycle counts, actuator torque, and seal integrity—and alerting operators to potential issues before a complete failure occurs. This allows for planned repairs during scheduled shutdowns, avoiding catastrophic failures and emergency service fees.

Moving from Reactive to Predictive
Traditional maintenance is either reactive (fix it when it breaks) or preventive (fix it on a calendar schedule). Both are costly. Reactive maintenance causes unplanned downtime. Preventive maintenance can lead to replacing parts that are still perfectly good.
Smart valves enable a predictive approach. They have built-in sensors that collect data on their own health.
Key Data Points for Prediction
Here is what smart valves monitor to predict problems:
- Operation Cycle Count: Tracks how many times the valve has opened and closed. This helps plan for wear-and-tear parts replacement.
- Actuator Torque Trends: Increasing torque needed to turn the valve can signal debris buildup, seal hardening, or impending mechanical failure.
- Seal and Leakage Diagnostics: Some advanced valves can detect subtle changes in performance that indicate a seal is beginning to degrade.
- Temperature and Vibration: Abnormal heat or vibration in the actuator can point to electrical or mechanical issues.
The Financial Advantage of Planned Repairs
When you get an alert that a valve is showing early signs of wear, you can order the part, schedule a technician, and address the issue during a planned maintenance window. This has huge cost benefits:
- No Emergency Fees: Technicians charge premium rates for emergency calls.
- No Overtime Labor: Work is done during normal hours.
- No Production Loss: The repair happens when the system is already offline.
- Prevents Cascade Damage: A small, fixed valve issue won’t escalate into a major pipe rupture or pump burn-out.
Cost of Downtime: Reactive vs. Predictive Maintenance
| Scenario | Reactive “Run-to-Failure” | Predictive “Monitor-to-Maintain” |
|---|---|---|
| Maintenance Trigger | Catastrophic valve failure stops the process. | System alerts on rising torque trend two weeks before failure. |
| Labor Cost | High emergency call-out fee, overtime pay. | Standard scheduled labor rate. |
| Parts Cost | Possible higher cost for expedited shipping. | Standard cost with planned delivery. |
| Downtime Cost | Extremely High. Unplanned, causing full production halt. | Very Low or Zero. Repaired during scheduled shutdown. |
| Secondary Damage | Likely (e.g., water damage, pump overload). | Unlikely, as failure is prevented. |
By predicting failures, smart valves turn maintenance from a costly, disruptive surprise into a planned, manageable event. This is one of the strongest ways they cut long-term operational expenses.
What Labor Savings Come from Remote Monitoring and Control Features?
Sending a technician to a remote site just to open or close a valve is a poor use of time and money. I’ve helped clients cut these routine site visits by over 80% with automation.
Remote monitoring and control create major labor savings by allowing a single operator to manage valves across multiple sites from a central dashboard. This eliminates countless hours spent on travel and manual valve operation for routine tasks, allowing field technicians to focus only on essential physical maintenance and complex repairs.

The High Cost of Manual Checks
In industries like water management, agriculture, or distributed manufacturing, valves can be spread over a wide area. Before automation, a technician had to drive from site to site to check readings, make adjustments, or perform shut-offs. This is inefficient, slow, and expensive.
Smart valves with IoT connectivity solve this problem. They bring the valve’s status and controls to the operator’s computer or smartphone.
How Remote Features Save Time and Money
The savings are realized in several key areas:
1. Elimination of Routine Travel:
An operator can now check the status of a valve 50 miles away in seconds. They can open, close, or adjust it with a click. What used to be a half-day trip for one task becomes a one-minute digital activity.
2. Faster Response to Alerts:
If a pressure sensor triggers an alarm, the operator can immediately close a specific smart valve to isolate a problem section. This speed minimizes potential damage and can be done long before a technician could arrive on site.
3. Optimized Technician Dispatch:
Instead of sending a technician out blind, remote diagnostics tell them exactly what the issue is. They can bring the right tool and part the first time, turning a potential two- or three-trip job into a single, efficient visit.
Labor Time Allocation: Before vs. After Automation
| Task Description | Traditional Manual System | With Smart Valve Automation |
|---|---|---|
| Daily/Weekly Valve Position Checks | Technician drives to each site (2-4 hours). | Operator checks all valves remotely (10 minutes). |
| Adjusting Flow for Seasonal Demand | Requires site visits to multiple valves. | Done instantly from the control room for all valves. |
| Responding to a Leak Alarm | Technician drives to site, locates manual valve, shuts it off (45+ min). | Operator identifies and closes the right valve remotely (2 minutes). |
| Diagnosing a Valve Problem | Technician visits site, performs tests (1-2 hours). | Operator reviews torque and cycle data remotely, plans repair (15 minutes). |
Freeing Up Skilled Labor
The biggest saving isn’t just in travel costs; it’s in the better use of human skills. Technicians are freed from mundane, repetitive tasks and can focus on higher-value work like system optimization, installing new equipment, or performing complex overhauls. This improves job satisfaction and overall operational effectiveness. In short, remote capabilities turn labor from a variable, travel-dependent cost into a fixed, efficient, and strategic resource.
How Does Leak Prevention Avoid Waste and Potential Damage Costs?
A small, undetected leak can cause massive damage. I’ve seen a leaking valve in a ceiling space that went unnoticed for months, leading to mold remediation and structural repairs that cost far more than the lost water.
Leak prevention avoids huge costs by using smart valves to automatically shut off flow when a leak is detected, minimizing the loss of expensive treated water or process fluids. More importantly, it prevents the secondary damage costs from flooding, mold, equipment corrosion, and facility downtime, which often dwarf the cost of the lost fluid itself.

The True Cost of a Leak
Many managers only consider the cost of the lost water or chemical. The real financial danger lies in what the leaking fluid does. Water damage to buildings, electrical systems, and inventory is devastating. A leak of corrosive or hazardous fluid poses even greater safety and environmental clean-up costs.
Smart valves act as the first and most critical line of automated defense.
The Mechanics of Automated Leak Prevention
Smart leak prevention systems work in a connected loop:
- Detection: Specialized sensors (acoustic, moisture, flow meters) detect abnormal conditions that indicate a leak.
- Communication: The sensor instantly sends an alarm signal to the building or process automation system.
- Automatic Action: The system identifies the smart valves controlling the affected zone and commands them to close automatically.
- Alert: Operators are notified that a leak has occurred and has been contained.
This entire process can happen in less than a minute, drastically limiting the volume of the leak.
Comparing Impact: Unchecked Leak vs. Automated Shut-off
| Consequence | Unchecked Manual System Leak | Automated Smart Valve Response |
|---|---|---|
| Fluid Loss Volume | Very High. Leaks until manually discovered and shut off (hours/days). | Very Low. Flow stops within minutes of detection. |
| Physical Damage | Severe. Flooding, mold, structural damage, ruined inventory. | Minimal to None. Leak is contained before major damage occurs. |
| Business Disruption | High. Facility may need to close for cleanup and repairs. | Low. Only the isolated section is affected; most operations continue. |
| Repair & Cleanup Cost | Extremely High. Includes water extraction, rebuilding, mold remediation. | Low. Limited to fixing the original leak point. |
| Insurance Implications | Premiums may rise after a major claim. May face liability issues. | Demonstrates risk mitigation, may help lower premiums. |
Proactive Monitoring for Micro-Leaks
Beyond catastrophic bursts, smart systems can also detect subtle, continuous micro-leaks by analyzing flow meter data. A small but constant trickle from a faulty seal can waste thousands of gallons and dollars per year. By identifying and flagging this trend, the system prompts maintenance for a tiny valve repair, preventing long-term waste.
In essence, smart valve automation treats leak prevention not as an afterthought, but as a core, automated function. It transforms the cost equation from a high-probability, high-impact risk to a low-probability, minimal-impact event. The savings from avoiding just one major flood incident can pay for the entire automation system many times over.
Conclusion
Smart valve automation cuts costs directly through energy savings, predictive maintenance, labor efficiency, and proactive leak prevention. For a reliable and cost-effective smart valve solution, explore IFAN’s range of automated valve products and system integration expertise.














Commentaires récents